The spatiotemporal expression and mineralization regulation of p75 neurotrophin receptor in the early tooth development
- PMID: 30357966
- PMCID: PMC6430448
- DOI: 10.1111/cpr.12523
The spatiotemporal expression and mineralization regulation of p75 neurotrophin receptor in the early tooth development
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Cell Prolif. 2022 Feb;55(2):e13171. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13171. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 35139251 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to investigate the spatiotemporal expression and potential role of p75NTR in tooth morphogenesis and tissue mineralization.
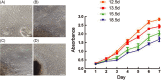
Materials and methods: The dynamic morphology of the four stages (from the beginning of E12.5 d, then E13.5 d and E15.5 d, to the end of E18.5 d) was observed, and the expressions of p75NTR and Runx2 were traced. The ectomesenchymal stem cells (EMSCs) were harvested in vitro, and the biological characteristics were observed. Moreover, the mineralization capability of EMSCs was evaluated. The relations between p75NTR and ALP, Col-1 and Runx2 were investigated.
Results: The morphologic results showed that the dental lamina appeared at E12.5 d, the bud stage at E13.5 d, the cap stage at E15.5 d and the bell stage at E18.5 d. p75NTR and Runx2 showed the similar expression pattern. EMSCs from the four stages showed no significant difference in proliferation. But the positive rate of p75NTR in the E12.5 d cells was significantly lower than that in the other three stages (P < 0.05). Moreover, the higher positive rate of p75NTR the cells were, the stronger mineralization capability they showed. p75NTR was well positively correlated with the mineralization-related markers ALP, Col-1 and Runx2, which increased gradually with the mature of dental germs.
Conclusion: p75NTR might play an important role in the regulation of tooth morphogenesis, especially dental hard tissue formation.
Keywords: ectomesenchymal stem cells; epithelial; mesenchymal interaction; mineralization; p75 neurotrophin receptor; tooth morphogenesis.
© 2018 The Authors. Cell Proliferation Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Moscatelli I, Pierantozzi E, Camaioni A, Siracusa G, Campagnolo L. p75 neurotrophin receptor is involved in proliferation of undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(18):3220‐3232. - PubMed
-
- Crane JF, Trainor PA. Neural crest stem and progenitor cells. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2006;22:267‐286. - PubMed
-
- Charalampopoulos I, Vicario A, Pediaditakis I, Gravanis A, Simi A, Ibáñez CF. Genetic dissection of neurotrophin signaling through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Cell Rep. 2012;2(6):1563‐1570. - PubMed
-
- Gentry JJ, Barker PA, Carter BD. The p75 neurotrophin receptor: multiple interactors and numerous functions. Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:25‐39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- cstc2016jcyjA0202/Chongqing Science and Technology Commission
- 2017ZDXM018/Key Project of Medical Research Program of Chongqing Municipal Health Bureau
- 81470032/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- CXTDG201602006/Program for Innovation Team Building at Institutions of Higher Education in Chongqing in 2016
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

