Novel application of metformin combined with targeted drugs on anticancer treatment
- PMID: 30358009
- PMCID: PMC6317954
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13849
Novel application of metformin combined with targeted drugs on anticancer treatment
Abstract
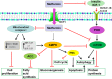
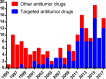
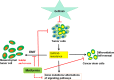
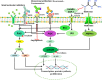
The success of targeted drug therapies for treating cancer patients has attracted broad attention both in the academic community and social society. However, rapidly developed acquired resistance is becoming a newly recognized major challenge to the continuing efficiency of these therapies. Metformin is a well-known natural compound with low toxicity derived from the plant French lilac. Our previous work has highlighted research progress of the combination of clinically applied chemotherapies and metformin by different mechanisms. We have also launched a study to combine metformin with the small molecule targeted drug gefitinib to treat bladder cancer using intravesical administration. Thus, in this minireview, we summarize recent achievements combining metformin with various targeted therapies. This work directs the potential clinical future by selecting available cancer patients and providing precise medicine by the combination of metformin and targeted drugs to overcome resistance and enhance therapeutic efficacies.
Keywords: combination; metformin; small molecular inhibitor; synergistic effect; targeted therapy.
© 2018 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metformin and gefitinib cooperate to inhibit bladder cancer growth via both AMPK and EGFR pathways joining at Akt and Erk.Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 23;6:28611. doi: 10.1038/srep28611. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27334428 Free PMC article.
-
High efficacy of intravesical treatment of metformin on bladder cancer in preclinical model.Oncotarget. 2016 Feb 23;7(8):9102-17. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.6933. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 26802022 Free PMC article.
-
Combinational strategies of metformin and chemotherapy in cancers.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016 Jul;78(1):13-26. doi: 10.1007/s00280-016-3037-3. Epub 2016 Apr 27. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27118574 Review.
-
Metformin sensitizes EGFR-TKI-resistant human lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo through inhibition of IL-6 signaling and EMT reversal.Clin Cancer Res. 2014 May 15;20(10):2714-26. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-2613. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24644001
-
Systemic therapy for metastatic bladder cancer in 2016 and beyond.Future Oncol. 2016 May;12(9):1179-92. doi: 10.2217/fon-2015-0020. Epub 2016 Feb 29. Future Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26922914 Review.
Cited by
-
Acquired drug resistance interferes with the susceptibility of prostate cancer cells to metabolic stress.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022 Nov 18;27(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s11658-022-00400-1. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36401206 Free PMC article.
-
Phase II clinical trial of metformin as a cancer stem cell-targeting agent in ovarian cancer.JCI Insight. 2020 Jun 4;5(11):e133247. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.133247. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32369446 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Lifestyle and Non-muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Recurrence, Progression, and Mortality: Available Research and Future Directions.Bladder Cancer. 2020;6(1):9-23. doi: 10.3233/blc-190249. Epub 2020 Mar 28. Bladder Cancer. 2020. PMID: 34095407 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of metformin and phenformin on apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in chemoresistant rectal cancer.Cancer Sci. 2019 Sep;110(9):2834-2845. doi: 10.1111/cas.14124. Epub 2019 Aug 2. Cancer Sci. 2019. PMID: 31278880 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin in combination with JS-K inhibits growth of renal cell carcinoma cells via reactive oxygen species activation and inducing DNA breaks.J Cancer. 2020 Mar 31;11(13):3701-3712. doi: 10.7150/jca.36372. eCollection 2020. J Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32328174 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quinn BJ, Kitagawa H, Memmott RM, et al. Repositioning metformin for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2013;24(9):469‐480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

