Polydatin suppresses nucleus pulposus cell senescence, promotes matrix homeostasis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats
- PMID: 30358118
- PMCID: PMC6201341
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.13848
Polydatin suppresses nucleus pulposus cell senescence, promotes matrix homeostasis and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats
Abstract
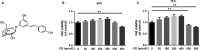
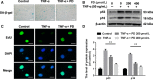
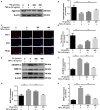
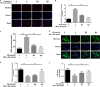
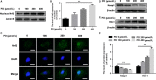
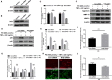
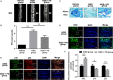
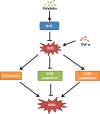
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD) is one of the major causes of low back pain. Polydatin (PD) has been shown to exert multiple pharmacological effects on different diseases; here, we test the therapeutic potential of PD for IVDD. In in-vitro experiments, we confirmed PD is nontoxic to nucleus pulposus cells (NPCs) under the concentration of 400 μmol/L. Furthermore, PD was able to decrease the level of senescence in TNF-α-treated NPCs, as indicated by β-gal staining as well as senescence markers p53 and p16 expression. In the aspect of extracellular matrix (ECM), PD not only reduced metalloproteinase 3 (MMP-3), metalloproteinase 13 (MMP-13) and a disintegrin-like and metalloproteinase thrombospondin type 1 motif 4 (ADAMTS-4) expression, but also increased aggrecan and collagen II levels. Mitochondrion is closely related to cellular senescence and ECM homeostasis; mechanistically, we found PD may rescue TNF-α-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, and it may also promote Nrf2 expression and activity. Silencing Nrf2 partly abolished the protective effects of PD on mitochondrial homeostasis, senescence and ECM homeostasis in TNF-α-treated NPCs. Correspondingly, PD ameliorated IVDD in rat model by promoting Nrf2 activity, preserving ECM and inhibiting senescence in nucleus pulposus cells. To sum up, our study suggests that PD exerts protective effects in NPCs against IVDD and reveals the underlying mechanism of PD on Nrf2 activation in NPCs.
Keywords: Nrf2; extracellular matrix; intervertebral disc degeneration; mitochondria; polydatin; senescence.
© 2018 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Senolytic agent Quercetin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the Nrf2/NF-κB axis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021 Mar;29(3):413-422. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2020.11.006. Epub 2020 Nov 23. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 33242601
-
Ginsenoside Rg1 relieves rat intervertebral disc degeneration and inhibits IL-1β-induced nucleus pulposus cell apoptosis and inflammation via NF-κB signaling pathway.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024 Mar;60(3):287-299. doi: 10.1007/s11626-024-00883-6. Epub 2024 Mar 14. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2024. PMID: 38485818 Free PMC article.
-
[Fibulin-3 Regulates Tissue Inhibitor of Metalloproteinases 3 to Inhibit Senescence in Intervertebral Disc Nucleus Pulposus Cells].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024 Sep 20;55(5):1217-1225. doi: 10.12182/20240760604. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2024. PMID: 39507955 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Exploration of the mode of death and potential death mechanisms of nucleus pulposus cells.Eur J Clin Invest. 2024 Sep;54(9):e14226. doi: 10.1111/eci.14226. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Eur J Clin Invest. 2024. PMID: 38632688 Review.
-
ASIC1a mediated nucleus pulposus cells pyroptosis and glycolytic crosstalk as a molecular basis for intervertebral disc degeneration.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 28;74(1):29. doi: 10.1007/s00011-025-02003-w. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39870819 Review.
Cited by
-
Metformin prevents the onset and progression of intervertebral disc degeneration: New insights and potential mechanisms (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2024 Aug;54(2):71. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2024.5395. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Int J Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 38963023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Nrf2 antioxidant defense system in intervertebral disc degeneration: Molecular insights.Exp Mol Med. 2022 Aug;54(8):1067-1075. doi: 10.1038/s12276-022-00829-6. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Exp Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35978054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel rat model of vertebral inflammation-induced intervertebral disc degeneration mediated by activating cGAS/STING molecular pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(20):9567-9585. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16898. Epub 2021 Sep 3. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34477314 Free PMC article.
-
Maslinic acid alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT and NF-κB signaling pathways.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024 May 25;56(5):776-788. doi: 10.3724/abbs.2024027. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2024. PMID: 38495003 Free PMC article.
-
Role of macrophage in intervertebral disc degeneration.Bone Res. 2025 Jan 23;13(1):15. doi: 10.1038/s41413-024-00397-7. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 39848963 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deyo RA, Mirza SK. CLINICAL PRACTICE. Herniated lumbar intervertebral disk. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1763. - PubMed
-
- Vergroesen PP, Kingma I, Emanuel KS, et al. Mechanics and biology in intervertebral disc degeneration: a vicious circle. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23:1057‐1070. - PubMed
-
- Liu W, Xia P, Feng J, et al. MicroRNA‐132 upregulation promotes matrix degradation in intervertebral disc degeneration. Exp Cell Res. 2017;359:39‐49. - PubMed
-
- Wang C, Yu X, Yan Y, et al. Tumor necrosis factor‐alpha: a key contributor to intervertebral disc degeneration. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2017;49:1‐13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

