HDAC8 inhibition ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 30358439
- PMCID: PMC6383499
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00551.2017
HDAC8 inhibition ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
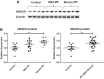
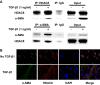
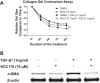
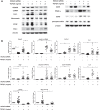
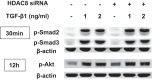
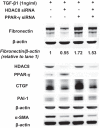
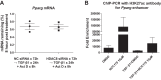
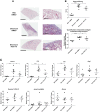
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a fibroproliferative lung disease, and fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation (FMD) is thought to be a key event in the pathogenesis of IPF. Histone deacetylase-8 (HDAC8) has been shown to associate with α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA; a marker of FMD) and regulates cell contractility in vascular smooth muscle cells. However, the role of HDAC8 in FMD or pulmonary fibrosis has never been reported. This study investigated the role of HDAC8 in pulmonary fibrosis with a focus on FMD. We observed that HDAC8 expression was increased in IPF lung tissue as well as transforming growth factor (TGF)β1-treated normal human lung fibroblasts (NHLFs). Immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that HDAC8 was associated with α-SMA in TGFβ1-treated NHLFs. HDAC8 inhibition with NCC170 (HDAC8-selective inhibitor) repressed TGFβ1-induced fibroblast contraction and α-SMA protein expression in NHLFs cultured in collagen gels. HDAC8 inhibition with HDAC8 siRNA also repressed TGFβ1-induced expression of profibrotic molecules such as fibronectin and increased expression of antifibrotic molecules such as peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ). Chromatin immunoprecipitation quantitative PCR using an antibody against H3K27ac (histone H3 acetylated at lysine 27; a known HDAC8 substrate and a marker for active enhancers) suggested that HDAC8 inhibition with NCC170 ameliorated TGFβ1-induced loss of H3K27ac at the PPARγ gene enhancer. Furthermore, NCC170 treatment significantly decreased fibrosis measured by Ashcroft score as well as expression of type 1 collagen and fibronectin in bleomycin-treated mouse lungs. These data suggest that HDAC8 contributes to pulmonary fibrosis and that there is a therapeutic potential for HDAC8 inhibitors to treat IPF as well as other fibrotic lung diseases.
Keywords: FMD; HDAC8; IPF; PPARγ; TGFβ1; bleomycin; fibronectin; type 1 collagen; α-SMA.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


References
-
- Burgess HA, Daugherty LE, Thatcher TH, Lakatos HF, Ray DM, Redonnet M, Phipps RP, Sime PJ. PPARγ agonists inhibit TGF-β-induced pulmonary myofibroblast differentiation and collagen production: implications for therapy of lung fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288: L1146–L1153, 2005. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00383.2004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Conforti F, Davies ER, Calderwood CJ, Thatcher TH, Jones MG, Smart DE, Mahajan S, Alzetani A, Havelock T, Maher TM, Molyneaux PL, Thorley AJ, Tetley TD, Warner JA, Packham G, Ganesan A, Skipp PJ, Marshall BJ, Richeldi L, Sime PJ, O’Reilly KMA, Davies DE. The histone deacetylase inhibitor, romidepsin, as a potential treatment for pulmonary fibrosis. Oncotarget 8: 48737–48754, 2017. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.17114. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davies ER, Haitchi HM, Thatcher TH, Sime PJ, Kottmann RM, Ganesan A, Packham G, O’Reilly KM, Davies DE. Spiruchostatin A inhibits proliferation and differentiation of fibroblasts from patients with pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 46: 687–694, 2012. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2011-0040OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deardorff MA, Bando M, Nakato R, Watrin E, Itoh T, Minamino M, Saitoh K, Komata M, Katou Y, Clark D, Cole KE, De Baere E, Decroos C, Di Donato N, Ernst S, Francey LJ, Gyftodimou Y, Hirashima K, Hullings M, Ishikawa Y, Jaulin C, Kaur M, Kiyono T, Lombardi PM, Magnaghi-Jaulin L, Mortier GR, Nozaki N, Petersen MB, Seimiya H, Siu VM, Suzuki Y, Takagaki K, Wilde JJ, Willems PJ, Prigent C, Gillessen-Kaesbach G, Christianson DW, Kaiser FJ, Jackson LG, Hirota T, Krantz ID, Shirahige K. HDAC8 mutations in Cornelia de Lange syndrome affect the cohesin acetylation cycle. Nature 489: 313–317, 2012. doi:10.1038/nature11316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- El Agha E, Moiseenko A, Kheirollahi V, De Langhe S, Crnkovic S, Kwapiszewska G, Szibor M, Kosanovic D, Schwind F, Schermuly RT, Henneke I, MacKenzie B, Quantius J, Herold S, Ntokou A, Ahlbrecht K, Braun T, Morty RE, Günther A, Seeger W, Bellusci S. Two-way conversion between lipogenic and myogenic fibroblastic phenotypes marks the progression and resolution of lung fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell 20: 261–273, .e3, 2017. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2016.10.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

