PINES: phenotype-informed tissue weighting improves prediction of pathogenic noncoding variants
- PMID: 30359302
- PMCID: PMC6203199
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-018-1546-6
PINES: phenotype-informed tissue weighting improves prediction of pathogenic noncoding variants
Abstract
Functional characterization of the noncoding genome is essential for biological understanding of gene regulation and disease. Here, we introduce the computational framework PINES (Phenotype-Informed Noncoding Element Scoring), which predicts the functional impact of noncoding variants by integrating epigenetic annotations in a phenotype-dependent manner. PINES enables analyses to be customized towards genomic annotations from cell types of the highest relevance given the phenotype of interest. We illustrate that PINES identifies functional noncoding variation more accurately than methods that do not use phenotype-weighted knowledge, while at the same time being flexible and easy to use via a dedicated web portal.
Keywords: Cell type specificity; Computational functionality prediction; Epigenetic annotations; Epigenetic regulation; Functional scoring; Noncoding variant; Phenotype-relevant scoring; Variant prioritization.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors have consented to the publication of this work in Genome Biology.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


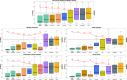
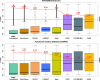

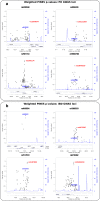
References
-
- Eiberg H, Troelsen J, Nielsen M, Mikkelsen A, Mengel-From J, Kjaer KW, Hansen L. Blue eye color in humans may be caused by a perfectly associated founder mutation in a regulatory element located within the herc2 gene inhibiting oca2 expression. Hum Genet. 2008;123(2):177–87. doi: 10.1007/s00439-007-0460-x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stavropoulos DJ, Merico D, Jobling R, Bowdin S, Monfared N, Thiruvahindrapuram B, Nalpathamkalam T, Pellecchia G, Yuen RK, Szego MJ, et al. Whole-genome sequencing expands diagnostic utility and improves clinical management in paediatric medicine. npj Genom Med. 2016;1:15012. doi: 10.1038/npjgenmed.2015.12. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

