Quantification of MicroRNAs by Coupling Cyclic Enzymatic Amplification with Microfluidic Voltage-Assisted Liquid Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 30359531
- PMCID: PMC6311092
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04008
Quantification of MicroRNAs by Coupling Cyclic Enzymatic Amplification with Microfluidic Voltage-Assisted Liquid Desorption Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
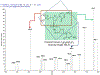
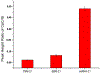
Quantitative assay of microRNAs (miRNAs) with mass spectrometric detection currently suffers from two major disadvantages, i.e., being insufficient in sensitivity and requiring an extraction or chromatographic separation prior to MS detection. In this work, we developed a facile and sensitive assay of targeted miRNAs based on the combination of cyclic enzymatic amplification (CEA) with microfluidic voltage-assisted liquid desorption electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (VAL-DESI-MS/MS). The single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) probe was designed to have a sequence complementary to the miRNA target with an extension of a two-base nucleotide fragment (i.e., CpC) at the 3'-position as MS signal reporter, thus being easy to prepare and high in stability. In the proposed CEA-VAL-DESI-MS/MS assay, an ssDNA probe was added to a sample solution, forming a DNA-miRNA hybrid. Duplex-specific nuclease (DSN) was then added to cleave specifically the DNA probe in the heteroduplex strands. As the hybridization-cleavage cycle repeated itself for many rounds, a large quantity of CpC molecules was produced that was quantified by VAL-DESI-MS/MS with accuracy and specificity. miRNA-21 was tested as the model target. The assay had a linear calibration equation in the range from 2.5 pM to 1.0 nM with a limit of detection of 0.25 pM. Determination of miRNA-21 in cellular samples was demonstrated. miRNA-21 was found to be 95.3 ± 13.95 amol ( n = 3) in 100 mouse peritoneal macrophages with a recovery of 94.2 ± 2.6% ( n = 3). Interestingly, analysis of exosomes secreted from these cells revealed that exposure of the cells to chemical stimuli caused a 3-fold increase in exosomal level of miRNA-21. The results suggest that the proposed assay may provide an accurate and cost-effective means for quantification of targeted miRNAs in biomedical samples.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
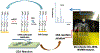

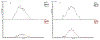
Similar articles
-
Mass spectrometric quantification of microRNAs in biological samples based on multistage signal amplification.Analyst. 2020 Mar 7;145(5):1783-1788. doi: 10.1039/c9an02064k. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Analyst. 2020. PMID: 31942587
-
Fast quantification of free amino acids in food by microfluidic voltage-assisted liquid desorption electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020 Mar;412(8):1947-1954. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02450-w. Epub 2020 Feb 4. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32020315 Free PMC article.
-
Duplex-Specific Nuclease-Mediated Amplification Strategy for Mass Spectrometry Quantification of MiRNA-200c in Breast Cancer Stem Cells.Anal Chem. 2019 Jul 16;91(14):8820-8826. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b04468. Epub 2019 Jun 27. Anal Chem. 2019. PMID: 31246422
-
Colorimetric and fluorescent dual-mode detection of microRNA based on duplex-specific nuclease assisted gold nanoparticle amplification.Analyst. 2019 Aug 21;144(16):4917-4924. doi: 10.1039/c9an01013k. Epub 2019 Jul 17. Analyst. 2019. PMID: 31313769
-
Direct Analysis of Biofluids by Mass Spectrometry with Microfluidic Voltage-Assisted Liquid Desorption Electrospray Ionization.Anal Chem. 2017 Nov 21;89(22):12014-12022. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b02398. Epub 2017 Nov 3. Anal Chem. 2017. PMID: 29065681 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
State-of-the-Art Fluorescent Probes: Duplex-Specific Nuclease-Based Strategies for Early Disease Diagnostics.Biosensors (Basel). 2022 Dec 15;12(12):1172. doi: 10.3390/bios12121172. Biosensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36551139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A triple signal amplification method for chemiluminescent detection of the cancer marker microRNA-21.Mikrochim Acta. 2019 Jun 10;186(7):410. doi: 10.1007/s00604-019-3537-z. Mikrochim Acta. 2019. PMID: 31183622
-
Faster, better, and cheaper: harnessing microfluidics and mass spectrometry for biotechnology.RSC Chem Biol. 2021 Jul 20;2(5):1331-1351. doi: 10.1039/d1cb00112d. eCollection 2021 Oct 7. RSC Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34704041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidics for detection of exosomes and microRNAs in cancer: State of the art.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022 Apr 27;28:758-791. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2022.04.011. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2022. PMID: 35664698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidic circulating reactor system for sensitive and automated duplex-specific nuclease-mediated microRNA detection.Talanta. 2021 Sep 1;232:122396. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122396. Epub 2021 Apr 20. Talanta. 2021. PMID: 34074392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shah IM; Macrae IM; Di Napoli M Neuroinflammation and neuroprotective strategies in acute ischaemic stroke-from bench to bedside. Curr. Mol. Med 2009, 9, 336–354. - PubMed
-
- Davies BP; Arenz C A homogenous assay for micro RNA maturation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2006, 45, 5550–5552. - PubMed
-
- Lagos-Quintana M; Rauhut R; Lendeckel W; Tuschl T Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 2001, 294, 853–858. - PubMed
-
- Várallyay É; Burgyán J; Havelda Z MicroRNA detection by northern blotting using locked nucleic acid probes. Nat. Protoc 2008, 3, 190–196. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

