Ixazomib promotes CHOP-dependent DR5 induction and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells
- PMID: 30359552
- PMCID: PMC6370389
- DOI: 10.1080/15384047.2018.1529095
Ixazomib promotes CHOP-dependent DR5 induction and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Ixazomib (Ninlaro), a novel proteasome inhibitor, has been developed for the treatment of many cancers and has demonstrated anti-tumor efficacy against various malignancies. However, the mechanism of the anti-tumor effect of ixazomib in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells remains unclear.
Methods: MTS and flow cytometry were performed to determine the effect of ixazomib on CRC cells. Western blotting and real-time RT-PCR were performed to detect ixazomib-induced DR5 upregulation. ChIP was performed to detect CHOP binding to DR5 promoter. Finally, xenograft experiments were carried out to measure the antitumor effect of ixazomib in vivo.
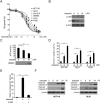
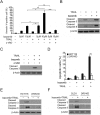
Results: In this study, we revealed the mechanism by which ixazomib inhibits the growth of CRC cells. Our findings indicated that ixazomib treatment induces CHOP-dependent DR5 induction, irrespective of p53 status. Furthermore, DR5 is necessary for ixazomib-mediated apoptosis. Ixazomib also synergized with TRAIL to induce marked apoptosis via DR5 in CRC cells.
Conclusions: Our findings further suggested that ixazomib sensitizes TRAIL/death receptor signaling pathway-targeted CRC and suggested that DR5 induction could be a valuable indicator of ixazomib sensitivity.
Keywords: CHOP; Ixazomib; TRAIL; death receptor 5; extrinsic apoptotic pathway.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
