β-Catenin expression is associated with cell invasiveness in pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 30360026
- PMCID: PMC6506732
- DOI: 10.3904/kjim.2017.155
β-Catenin expression is associated with cell invasiveness in pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background/aims: This study was tried to determine the role of β-catenin in invasion in pancreatic cancer.
Methods: We analyzed cancer invasiveness according to β-catenin expression in pancreatic cancer cell line. We also investigated the change in cancer invasiveness when β-catenin expression was changed. To enhance β-catenin activity, we treated low β-catenin cancer cell line, PANC1, with Wnt-3a conditioned media and transected β-catenin. We also treated high β-catenin expressing cell line, BxPC3, with XAV939, β-catenin inhibitor and siRNA for β-catenin to inhibit β-catenin expression.
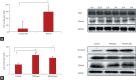
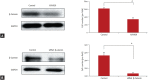
Results: The high β-catenin expressing cancer cell line, BxPC3 showed higher invasiveness, and low β-catenin expressing cell lines, PANC1and MIA-PaCa-2, were less invasive. By adding the Wnt-3a conditioned media or performing transfection with β-catenin in PANC1, cell invasiveness was increased (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). On inhibition of β-catenin by XAV939 and siRNA in BxPC3 cell line, invasiveness was significantly decreased (p < 0.01). It was not correlated with the expression of cluster of differentiation 44 (CD44) or CD44 variant 6 (CD44v6), the invasion related protein. On analysis of association with metastasis in human tissue, Wnt-3a expression was statistically correlated with the development of metastasis (p = 0.029).
Conclusion: Based on our data, β-catenin may be involved in cancer invasion in pancreatic cancer, and it is not associated with CD44, the invasion related protein.
Keywords: Beta-catenin; Invasiveness; Pancreatic neoplasms.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Rab11a sustains GSK3β/Wnt/β-catenin signaling to enhance cancer progression in pancreatic cancer.Tumour Biol. 2016 Oct;37(10):13821-13829. doi: 10.1007/s13277-016-5172-1. Epub 2016 Aug 1. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 27481517
-
KiSS‑1‑mediated suppression of the invasive ability of human pancreatic carcinoma cells is not dependent on the level of KiSS‑1 receptor GPR54.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Jan;13(1):123-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4535. Epub 2015 Nov 9. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 26572251 Free PMC article.
-
Gamma-Secretase Inhibitor IX (GSI) Impairs Concomitant Activation of Notch and Wnt-Beta-Catenin Pathways in CD44+ Gastric Cancer Stem Cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017 Mar;6(3):819-829. doi: 10.1002/sctm.16-0335. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017. PMID: 28186678 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of LRRFIP1 reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Cancer Lett. 2015 Aug 28;365(1):132-40. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.05.023. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 26047573
-
ZNF281 Promotes Growth and Invasion of Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.Dig Dis Sci. 2017 Aug;62(8):2011-2020. doi: 10.1007/s10620-017-4611-1. Epub 2017 May 18. Dig Dis Sci. 2017. PMID: 28523575
Cited by
-
Implication of ERBB2 as a Predictive Tool for Survival in Patients with Pancreatic Cancer in Histological Studies.Curr Oncol. 2022 Mar 30;29(4):2442-2453. doi: 10.3390/curroncol29040198. Curr Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35448172 Free PMC article.
-
ROS-dependent HIF1α activation under forced lipid catabolism entails glycolysis and mitophagy as mediators of higher proliferation rate in cervical cancer cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Mar 11;40(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-01887-w. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33706793 Free PMC article.
-
Drug Combinations: A New Strategy to Extend Drug Repurposing and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Breast and Colon Cancer Cells.Biomolecules. 2022 Jan 23;12(2):190. doi: 10.3390/biom12020190. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35204691 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of the System-Level Mechanisms of the Herbal Drug FDY003 for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment: A Network Pharmacological Investigation.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 May 10;2022:7160209. doi: 10.1155/2022/7160209. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35591866 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolin Targeting by N6L Inhibits Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 15;13(12):2986. doi: 10.3390/cancers13122986. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34203710 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Sugiura T, Uesaka K, Mihara K, et al. Margin status, recurrence pattern, and prognosis after resection of pancreatic cancer. Surgery. 2013;154:1078–1086. - PubMed
-
- Oettle H, Neuhaus P, Hochhaus A, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy with gemcitabine and long-term outcomes among patients with resected pancreatic cancer: the CONKO-001 randomized trial. JAMA. 2013;310:1473–1481. - PubMed
-
- Tenbaum SP, Ordonez-Moran P, Puig I, et al. β-Catenin confers resistance to PI3K and AKT inhibitors and subverts FOXO3a to promote metastasis in colon cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18:892–901. - PubMed
-
- Du Y, Wang Y, Zhang F, et al. Regulation of metastasis of bladder cancer cells through the WNT signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 2015;36:8839–8844. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
