Acute kidney injury and continuous renal replacement therapy in children; what pediatricians need to know
- PMID: 30360040
- PMCID: PMC6258966
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2018.06996
Acute kidney injury and continuous renal replacement therapy in children; what pediatricians need to know
Abstract
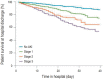
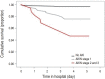
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is characterized by abrupt deterioration of renal function, and its diagnosis relies on creatinine measurements and urine output. AKI is associated with higher morbidity and mortality, and is a risk factor for development of chronic kidney disease. There is no proven medication for AKI. Therefore, prevention and early detection are important. Physicians should be aware of the risk factors for AKI and should monitor renal function in high-risk patients. Management of AKI includes optimization of volume status and renal perfusion, avoidance of nephrotoxic agents, and sufficient nutritional support. Continuous renal replacement therapy is widely available for critically ill children, and this review provides basic information regarding this therapy. Long-term follow-up of patients with AKI for renal function, blood pressure, and proteinuria is recommended.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Child; Renal replacement therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Rewa O, Bagshaw SM. Acute kidney injury-epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2014;10:193–207. - PubMed
-
- Selewski DT, Charlton JR, Jetton JG, Guillet R, Mhanna MJ, Askenazi DJ, et al. Neonatal Acute Kidney Injury. Pediatrics. 2015;136:e463. - PubMed
-
- Nehus EJ, Laskin BL, Kathman TI, Bissler JJ. Performance of cystatin C-based equations in a pediatric cohort at high risk of kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol. 2013;28:453–61. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

