Application of Molecular Methods in the Identification of Ingredients in Chinese Herbal Medicines
- PMID: 30360419
- PMCID: PMC6222746
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23102728
Application of Molecular Methods in the Identification of Ingredients in Chinese Herbal Medicines
Abstract
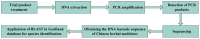
There are several kinds of Chinese herbal medicines originating from diverse sources. However, the rapid taxonomic identification of large quantities of Chinese herbal medicines is difficult using traditional methods, and the process of identification itself is prone to error. Therefore, the traditional methods of Chinese herbal medicine identification must meet higher standards of accuracy. With the rapid development of bioinformatics, methods relying on bioinformatics strategies offer advantages with respect to the speed and accuracy of the identification of Chinese herbal medicine ingredients. This article reviews the applicability and limitations of biochip and DNA barcoding technology in the identification of Chinese herbal medicines. Furthermore, the future development of the two technologies of interest is discussed.
Keywords: DNA barcoding technology; biochip technology; bioinformatics; identification of Chinese herbal medicines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The founding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
-
- Han J., Song J., Yao H., Chen X., Chen S. Comparison of DNA barcoders in identifying medicinal materials. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012;37:1056–1061. - PubMed
-
- Qian Z., Lin C.R., Xiao P.G. Identification and standard of traditional Chinese Medicine. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2014;39:2153–2154.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources