Current Therapies Focused on High-Density Lipoproteins Associated with Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 30360466
- PMCID: PMC6278283
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23112730
Current Therapies Focused on High-Density Lipoproteins Associated with Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
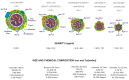
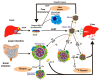
High-density lipoproteins (HDL) comprise a heterogeneous family of lipoprotein particles divided into subclasses that are determined by density, size and surface charge as well as protein composition. Epidemiological studies have suggested an inverse correlation between High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol (HDL-C) levels and the risk of cardiovascular diseases and atherosclerosis. HDLs promote reverse cholesterol transport (RCT) and have several atheroprotective functions such as anti-inflammation, anti-thrombosis, and anti-oxidation. HDLs are considered to be atheroprotective because they are associated in serum with paraoxonases (PONs) which protect HDL from oxidation. Polyphenol consumption reduces the risk of chronic diseases in humans. Polyphenols increase the binding of HDL to PON1, increasing the catalytic activity of PON1. This review summarizes the evidence currently available regarding pharmacological and alternative treatments aimed at improving the functionality of HDL-C. Information on the effectiveness of the treatments has contributed to the understanding of the molecular mechanisms that regulate plasma levels of HDL-C, thereby promoting the development of more effective treatment of cardiovascular diseases. For that purpose, Scopus and Medline databases were searched to identify the publications investigating the impact of current therapies focused on high-density lipoproteins.
Keywords: HDL-C; lipoproteins; paraoxonase; polyphenols.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of nonstatin lipid drug therapy on high-density lipoprotein metabolism.Am J Cardiol. 2003 Apr 3;91(7A):18E-23E. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(02)03384-2. Am J Cardiol. 2003. PMID: 12679199 Review.
-
Pharmacologic elevation of high-density lipoproteins: recent insights on mechanism of action and atherosclerosis protection.Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004 Jul;19(4):366-73. doi: 10.1097/01.hco.0000126582.27767.87. Curr Opin Cardiol. 2004. PMID: 15218398 Review.
-
Targeting high-density lipoproteins: update on a promising therapy.Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2013 Nov;106(11):601-11. doi: 10.1016/j.acvd.2013.06.052. Epub 2013 Sep 25. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2013. PMID: 24074699
-
HDL-Targeting Therapeutics: Past, Present and Future.Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(8):1207-1215. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161027153140. Curr Pharm Des. 2017. PMID: 27799042 Review.
-
Statins and metabolism of high density lipoprotein.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2007 Jul;5(3):215-21. doi: 10.2174/187152507781058672. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17630948 Review.
Cited by
-
[Dysfunctional high-density lipoproteins in diabetes mellitus].Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 2022 Jun 10;68(4):69-77. doi: 10.14341/probl13118. Probl Endokrinol (Mosk). 2022. PMID: 36104968 Free PMC article. Russian.
-
Post-translational modifications of S1PR1 and endothelial barrier regulation.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020 Sep;1865(9):158760. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2020.158760. Epub 2020 Jun 22. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2020. PMID: 32585303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Micromethod for Polyphenol High-Throughput Screening Saves 90 Percent Reagents and Sample Volume.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 Dec 21;9(1):11. doi: 10.3390/antiox9010011. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31877807 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammation and Oxidative Stress Induced by Obesity, Gestational Diabetes, and Preeclampsia in Pregnancy: Role of High-Density Lipoproteins as Vectors for Bioactive Compounds.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 23;12(10):1894. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101894. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37891973 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Paraoxonases Activities and Polymorphisms in Elderly and Old-Age Diseases: An Overview.Antioxidants (Basel). 2019 May 2;8(5):118. doi: 10.3390/antiox8050118. Antioxidants (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31052559 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mahley R.W., Innerarity T.L., Rall S.C., Weisgraber K.H. Plasma lipoproteins: Apolipoprotein structure and function. J. Lipid Res. 1984;25:1277–1294. - PubMed
-
- Mahley R.W., Ji Z.S. Remnant lipoprotein metabolism: Key pathways involving cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycans and apolipoprotein E. J. Lipid Res. 1999;40:1–16. - PubMed
-
- Segrest J.P., Jones M.K., De Loof H., Dashti N. Structure of apolipoprotein B-100 in low density lipoproteins. J. Lipid Res. 2001;42:1346–1367. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

