The Acute Toxicity of Tetrodotoxin and Tetrodotoxin⁻Saxitoxin Mixtures to Mice by Various Routes of Administration
- PMID: 30360529
- PMCID: PMC6266834
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10110423
The Acute Toxicity of Tetrodotoxin and Tetrodotoxin⁻Saxitoxin Mixtures to Mice by Various Routes of Administration
Abstract
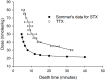
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) is a potent neurotoxin associated with human poisonings through the consumption of pufferfish. More recently, TTX has been identified in bivalve molluscs from diverse geographical environments, including Europe, and is therefore recognised as an emerging threat to food safety. A recent scientific opinion of the EFSA Panel on Contaminants in the Food Chain recognised the need for further data on the acute oral toxicity of TTX and suggested that, since saxitoxin (STX) and TTX had similar modes of action, it was possible that their toxicities were additive so could perhaps be combined to yield one health-based guideline value. The present study determined the toxicity of TTX by various routes of administration. The testing of three different mixtures of STX and TTX and comparing the experimentally determined values to those predicted on the basis of additive toxicity demonstrated that the toxicities of STX and TTX are additive. This illustrates that it is appropriate to treat TTX as a member of the paralytic shellfish group of toxins. Since the toxicity of TTX was found to be the same as STX by feeding, a molar toxicity equivalence factor of 1.0 for TTX can be applied.
Keywords: acute toxicity; oral toxicity; paralytic shellfish toxins; saxitoxin; tetrodotoxin; toxicity equivalence factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Sub-Acute Dosing Study of Saxitoxin and Tetrodotoxin Mixtures in Mice Suggests That the Current Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Regulatory Limit Is Fit for Purpose.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jul 3;15(7):437. doi: 10.3390/toxins15070437. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37505706 Free PMC article.
-
Oral Chronic Toxicity of the Safe Tetrodotoxin Dose Proposed by the European Food Safety Authority and Its Additive Effect with Saxitoxin.Toxins (Basel). 2020 May 9;12(5):312. doi: 10.3390/toxins12050312. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32397553 Free PMC article.
-
Tetrodotoxin in marine bivalves and edible gastropods: A mini-review.Chemosphere. 2019 Dec;236:124404. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124404. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Chemosphere. 2019. PMID: 31545201 Review.
-
Co-Occurrence of Tetrodotoxin and Saxitoxins and Their Intra-Body Distribution in the Pufferfish Canthigaster valentini.Toxins (Basel). 2020 Jul 3;12(7):436. doi: 10.3390/toxins12070436. Toxins (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32635254 Free PMC article.
-
Binding and Pharmacokinetics of the Sodium Channel Blocking Toxins (Saxitoxin and the Tetrodotoxins).Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017;17(4):320-327. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 27306745 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation, invitro, invivo anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antioxidant potential of Habenaria plantegania Lindl.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Apr;32(2):1353-1369. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01425-4. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38334860
-
A Sub-Acute Dosing Study of Saxitoxin and Tetrodotoxin Mixtures in Mice Suggests That the Current Paralytic Shellfish Toxin Regulatory Limit Is Fit for Purpose.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Jul 3;15(7):437. doi: 10.3390/toxins15070437. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37505706 Free PMC article.
-
Past, Current and Future Techniques for Monitoring Paralytic Shellfish Toxins in Bivalve Molluscs.Toxins (Basel). 2025 Feb 25;17(3):105. doi: 10.3390/toxins17030105. Toxins (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40137878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Cyclic Imines in Shellfish: Worldwide Occurrence, Toxicity and Assessment of the Risk to Consumers.Mar Drugs. 2024 Mar 11;22(3):129. doi: 10.3390/md22030129. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38535470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of Succinimide Derivative as a Multi-Target, Anti-Diabetic Agent: In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches.Molecules. 2023 Feb 7;28(4):1589. doi: 10.3390/molecules28041589. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36838577 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hwang D.F., Noguchi T. Advances in Food and Nutrition Research. Volume 52. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2007. Tetrodotoxin Poisoning; pp. 141–236. - PubMed
-
- Hwang P.-A., Tsai Y.-H., Lin S.-J., Hwang D.-F. The Gastropods Possessing TTX and/or PSP. Food Rev. Int. 2007;23:321–340. doi: 10.1080/87559120701418384. - DOI
-
- Hwang D.F., Tsai Y.H. Toxins in toxic Taiwanese crabs. Food Rev. Int. 1999;15:145–162. doi: 10.1080/87559129909541184. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases