Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology
- PMID: 30361278
- PMCID: PMC6362807
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2018-313173
Artificial intelligence and deep learning in ophthalmology
Abstract
Artificial intelligence (AI) based on deep learning (DL) has sparked tremendous global interest in recent years. DL has been widely adopted in image recognition, speech recognition and natural language processing, but is only beginning to impact on healthcare. In ophthalmology, DL has been applied to fundus photographs, optical coherence tomography and visual fields, achieving robust classification performance in the detection of diabetic retinopathy and retinopathy of prematurity, the glaucoma-like disc, macular oedema and age-related macular degeneration. DL in ocular imaging may be used in conjunction with telemedicine as a possible solution to screen, diagnose and monitor major eye diseases for patients in primary care and community settings. Nonetheless, there are also potential challenges with DL application in ophthalmology, including clinical and technical challenges, explainability of the algorithm results, medicolegal issues, and physician and patient acceptance of the AI 'black-box' algorithms. DL could potentially revolutionise how ophthalmology is practised in the future. This review provides a summary of the state-of-the-art DL systems described for ophthalmic applications, potential challenges in clinical deployment and the path forward.
Keywords: glaucoma; imaging; public health; retina; telemedicine.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2019. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: DSWT and TYW are the coinventors of a deep learning system for retinal diseases. LP is a member of Google AI Healthcare. LRP is a non-paid consultant for Visulytix. PAK is a consultant for DeepMind.
Figures
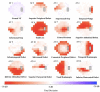
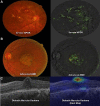
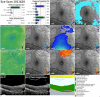
References
-
- World Economic Forum , 2016. The fourth industrial revolution: what it means, how to respond. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2016/01/the-fourth-industrial-revolution-... (accessed 18 Aug 2018).
-
- Tompson J, Jain A, LeCun Y. Joint training of a convolutional network and a graphical model for human pose estimation. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 2014;27:1799–807.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
