DUET: A Phase 2 Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Sparsentan in Patients with FSGS
- PMID: 30361325
- PMCID: PMC6218860
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2018010091
DUET: A Phase 2 Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Sparsentan in Patients with FSGS
Erratum in
-
Erratum.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019 Mar;30(3):518. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019010051. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 36632636 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: We evaluated and compared the effects of sparsentan, a dual endothelin type A (ETA) and angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist, with those of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with primary FSGS.
Methods: In this phase 2, randomized, double-blind, active-control Efficacy and Safety of Sparsentan (RE-021), a Dual Endothelin Receptor and Angiotensin Receptor Blocker, in Patients with Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS): A Randomized, Double-blind, Active-Control, Dose-Escalation Study (DUET), patients aged 8-75 years with biopsy-proven FSGS, eGFR>30 ml/min per 1.73 m2, and urinary protein-to-creatinine ratio (UP/C) ≥1.0 g/g received sparsentan (200, 400, or 800 mg/d) or irbesartan (300 mg/d) for 8 weeks, followed by open-label sparsentan only. End points at week 8 were reduction from baseline in UP/C (primary) and proportion of patients achieving FSGS partial remission end point (FPRE) (UP/C: ≤1.5 g/g and >40% reduction [secondary]).
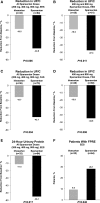
Results: Of 109 patients randomized, 96 received study drugs and had baseline and week 8 UP/C measurements. Sparsentan-treated patients had greater reductions in UP/C than irbesartan-treated patients did when all doses (45% versus 19%; P=0.006) or the 400 and 800 mg doses (47% versus 19%; P=0.01) were pooled for analysis. The FSGS partial remission end point was achieved in 28% of sparsentan-treated and 9% of irbesartan-treated patients (P=0.04). After 8 weeks of treatment, BP was reduced with sparsentan but not irbesartan, and eGFR was stable with both treatments. Overall, the incidence of adverse events was similar between groups. Hypotension and edema were more common among sparsentan-treated patients but did not result in study withdrawals.
Conclusions: Patients with FSGS achieved significantly greater reductions in proteinuria after 8 weeks of sparsentan versus irbesartan. Sparsentan was safe and well tolerated.
Keywords: angiotensin II; endothelin; focal segmental glomerulosclerosis; proteinuria; sparsentan.
Copyright © 2018 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


References
-
- D’Agati VD, Kaskel FJ, Falk RJ: Focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. N Engl J Med 365: 2398–2411, 2011 - PubMed
-
- Zand L, Glassock RJ, De Vriese AS, Sethi S, Fervenza FC: What are we missing in the clinical trials of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant 32[Suppl 1]: i14–i21, 2017 - PubMed
-
- Rosenberg AZ, Naicker S, Winkler CA, Kopp JB: HIV-associated nephropathies: Epidemiology, pathology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrol 11: 150–160, 2015 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

