The chromatin accessibility landscape of primary human cancers
- PMID: 30361341
- PMCID: PMC6408149
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aav1898
The chromatin accessibility landscape of primary human cancers
Abstract
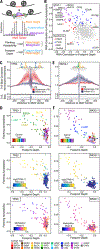
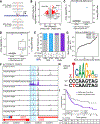
We present the genome-wide chromatin accessibility profiles of 410 tumor samples spanning 23 cancer types from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We identify 562,709 transposase-accessible DNA elements that substantially extend the compendium of known cis-regulatory elements. Integration of ATAC-seq (the assay for transposase-accessible chromatin using sequencing) with TCGA multi-omic data identifies a large number of putative distal enhancers that distinguish molecular subtypes of cancers, uncovers specific driving transcription factors via protein-DNA footprints, and nominates long-range gene-regulatory interactions in cancer. These data reveal genetic risk loci of cancer predisposition as active DNA regulatory elements in cancer, identify gene-regulatory interactions underlying cancer immune evasion, and pinpoint noncoding mutations that drive enhancer activation and may affect patient survival. These results suggest a systematic approach to understanding the noncoding genome in cancer to advance diagnosis and therapy.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures





Comment in
-
The chromatin of cancer.Science. 2018 Oct 26;362(6413):401-402. doi: 10.1126/science.aav3494. Science. 2018. PMID: 30361360 No abstract available.
-
Cancer chromatin accessed.Nat Rev Genet. 2019 Jan;20(1):5. doi: 10.1038/s41576-018-0075-1. Nat Rev Genet. 2019. PMID: 30429584 No abstract available.
-
Cancer chromatin accessed.Nat Rev Cancer. 2019 Jan;19(1):7. doi: 10.1038/s41568-018-0088-2. Nat Rev Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30487581 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U24 CA210978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 AG059918/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHMI/Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- U24 CA210950/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA194547/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA180951/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HG007735/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210974/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210989/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210952/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000044/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 HG009436/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210949/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210990/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA209919/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210969/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA210988/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States

