Binocular disparity can augment the capacity of vision without affecting subjective experience of depth
- PMID: 30361498
- PMCID: PMC6202414
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-34137-9
Binocular disparity can augment the capacity of vision without affecting subjective experience of depth
Abstract
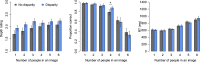
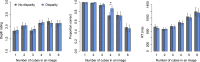
Binocular disparity results in a tangible subjective experience of three-dimensional world, but whether disparity also augments objective perceptual performance remains debated. We hypothesized that the improved coding of depth enabled by binocular disparity allows participants to individuate more objects at a glance as the objects can be more efficiently differentiated from each other and the background. We asked participants to enumerate objects in briefly presented naturalistic (Experiment 1) and artificial (Experiment 2) scenes in immersive virtual reality. This type of enumeration task yields well-documented capacity limits where up to 3-4 items can be enumerated rapidly and accurately, known as subitizing. Our results show that although binocular disparity did not yield a large general improvement in enumeration accuracy or reaction times, it improved participants' ability to process the items right after the limit of perceptual capacity. Binocular disparity also sped-up response times by 27 ms on average when artificial stimuli (cubes) were used. Interestingly, the influence of disparity on subjectively experienced depth revealed a clearly different pattern than the influence of disparity on objective performance. This suggests that the functional and subjective sides of stereopsis can be dissociated. Altogether our results suggest that binocular disparity may increase the number of items the visual system can simultaneously process. This may help animals to better resolve and track objects in complex, cluttered visual environments.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Volume perception: Disparity extraction and depth representation in complex three-dimensional environments.J Vis. 2014 Oct 13;14(12):11. doi: 10.1167/14.12.11. J Vis. 2014. PMID: 25761279
-
Seeing in 3-d with just one eye: stereopsis without binocular vision.Psychol Sci. 2013 Sep;24(9):1673-85. doi: 10.1177/0956797613477867. Epub 2013 Jul 26. Psychol Sci. 2013. PMID: 23892232
-
Relating visual and pictorial space: Integration of binocular disparity and motion parallax.J Vis. 2024 Dec 2;24(13):7. doi: 10.1167/jov.24.13.7. J Vis. 2024. PMID: 39652056 Free PMC article.
-
The role of monocularly visible regions in depth and surface perception.Vision Res. 2009 Nov;49(22):2666-85. doi: 10.1016/j.visres.2009.06.021. Epub 2009 Jul 3. Vision Res. 2009. PMID: 19577589 Review.
-
Configuration stereopsis: a new look at the depth-disparity relation.Spat Vis. 2009;22(1):91-103. doi: 10.1163/156856809786618493. Spat Vis. 2009. PMID: 19055889 Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of binocular disparity on learning anatomy with stereoscopic augmented reality visualization: A double center randomized controlled trial.Anat Sci Educ. 2023 Jan;16(1):87-98. doi: 10.1002/ase.2164. Epub 2022 Mar 18. Anat Sci Educ. 2023. PMID: 34894205 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Heesy CP. Seeing in stereo: The ecology and evolution of primate binocular vision and stereopsis. Evolutionary Anthropology. 2009;18:21–35. doi: 10.1002/evan.20195. - DOI
-
- Barry, S. R. Fixing My Gaze (Basic Books, New York, 2009).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

