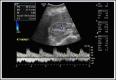
Renal resistive index in hypertensive patients
- PMID: 30362245
- PMCID: PMC8031325
- DOI: 10.1111/jch.13410
Renal resistive index in hypertensive patients
Abstract
Spectral Doppler ultrasonography provides the evaluation of renal resistive index (RRI), a noninvasive and reproducible measure to investigate arterial compliance and/or resistance. RRI seems to possess an important role in the evaluation of diverse cases of secondary hypertension. In essential hypertension, RRI is associated with subclinical markers of target organ damage and reflects renal disease progression beyond albuminuria and creatinine clearance. Also, RRI can estimate cardiovascular and renal risk. The evaluation of RRI may also help the therapeutic decisions. Given its simple assessment, RRI emerges as a simple method and a "multifunctional" tool that could help on the cardiovascular risk evaluation of the hypertensive patient.
Keywords: hypertensive nephropathy; renal disease; renal hemodynamics; renal resistive index.
©2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Radermacher J, Ellis S, Haller H. Renal resistance index and progression of renal disease. Hypertension. 2002;39:699‐703. - PubMed
-
- Ponte B, Pruijm M, Ackermann D, et al. Reference values and factors associated with renal resistive index in a family‐based population study. Hypertension. 2014;63:136‐142. - PubMed
-
- Boddi M. Renal ultrasound (and Doppler sonography) in hypertension: an update. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;956:191‐208. - PubMed
-
- Hashimoto J, Ito S. Central pulse pressure and aortic stiffness determine renal hemodynamics: pathophysiological implication for microalbuminuria in hypertension. Hypertension. 2011;58:839‐846. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical