Tension pneumocephalus: the neurosurgical emergency equivalent of tension pneumothorax
- PMID: 30363668
- PMCID: PMC6180885
- DOI: 10.1259/bjrcr.20150127
Tension pneumocephalus: the neurosurgical emergency equivalent of tension pneumothorax
Abstract
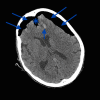
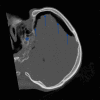
Tension pneumocephalus (TP) is the intracranial equivalent of tension pneumothorax. It is an unusual but life-threatening neurosurgical emergency, which has been described following head trauma, epidural injections or complicating neurological, spinal, craniofacial or sinus surgery. Unfortunately, the signs and symptoms of TP are non-specific and the diagnosis must be made by prompt recognition of the classic imaging signs of TP, allowing lifesaving emergency decompression. We present a trauma patient demonstrating the "Mount Fuji" sign on an unenhanced CT scan of the brain, which is reportedly specific for TP.
Figures
References
-
- Michel SJ. The Mount Fuji sign. Radiology 2004; 232: 449–50. - PubMed
-
- Swan MC, Scholz AFM, Pretorius PM, Johnson D, Martinez-Devesa P, Wall SA. Lessons in the management of post-operative tension pneumocephalus complicating transcranial resection of advanced cutaneous tumours with free flap reconstruction. J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2013; 41: 850–5. - PubMed
-
- Sweni S, Senthilkumaran S, Balamurugan N, Thirumalaikolundusubramanian P. Tension pneumocephalus: a case report with review of literature. Emerg Radiol 2013; 20: 573–8. - PubMed
-
- Monas J, Peak DA. Spontaneous tension pneumocephalus resulting from a scalp fistula in a patient with a remotely placed ventriculoperitoneal shunt. Ann Emerg Med 2010; 56: 378–81. - PubMed
-
- Ishiwata Y, Fujitsu K, Sekino T, Fujino H, Kubokura T, Tsubone K, et al. . Subdural tension pneumocephalus following surgery for chronic subdural hematoma. J Neurosurg 1988; 68: 58–61. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

