Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to acute cholecystitis: an unusual cause for haemobilia
- PMID: 30363671
- PMCID: PMC6180884
- DOI: 10.1259/bjrcr.20150423
Cystic artery pseudoaneurysm secondary to acute cholecystitis: an unusual cause for haemobilia
Abstract
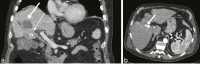
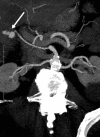
Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery is a rarely described cause of haemobilia. We report the unusual presentation of upper gastrointestinal haemorrhage due to a pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery secondary to acute cholecystitis that was complicated by gallbladder perforation and liver abscess in an 88-year-old male. The original CT scan had demonstrated a high density focus in the gallbladder neck that was thought to represent a calculus. Selective embolization of the cystic artery resulted in cessation of the haemorrhage. Owing to the patient's frailty and comorbidities, he was not considered suitable for cholecystectomy. The case emphasizes the need for a high level of awareness of pseudoaneurysmal disease in association with inflammatory conditions.
Figures

References
-
- Akatsu T, Tanabe M, Shimizu T, Handa K, Kawachi S, Aiura K, et al. . Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery secondary to cholecystitis as a cause of hemobilia: report of a case. Surg Today 2007; 37: 412–17. - PubMed
-
- Muñoz-Villafranca C, García-Kamirruaga Í, Góme-García P, Atín-del-Campo V, Bárcena-Robredo V, Aguinaga-Alesanco A, et al. . Pseudoaneurysm of the cystic artery: an uncommon cause of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in a case of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis. Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2015; 107: 375–6. - PubMed
-
- Curet P, Baumer R, Roche A, Grellet J, Mercadier M. Hepatic hemobilia of traumatic or iatrogenic origin: recent advances in diagnosis and therapy, review of the literature from 1976 to 1981. World J Surg 1984; 8: 2–8. - PubMed
-
- Croce MA, Fabian TC, Spiers JP, Kudsk KA. Traumatic hepatic artery pseudoaneurysm with hemobilia. AM J Surg 1994; 168: 235–8. - PubMed
-
- Mori M, Kohzaki S, Makino K, Amamoto Y, Mori M, Kanbara C, et al. . Spontaneous intracholecystic hemorrhage due to polyarteritis nodosa. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1998; 22: 730–1. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

