Murine DX5+NKT Cells Display Their Cytotoxic and Proapoptotic Potentials against Colitis-Inducing CD4+CD62Lhigh T Cells through Fas Ligand
- PMID: 30364054
- PMCID: PMC6186349
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/8175810
Murine DX5+NKT Cells Display Their Cytotoxic and Proapoptotic Potentials against Colitis-Inducing CD4+CD62Lhigh T Cells through Fas Ligand
Abstract
Introduction: It has been previously shown that immunoregulatory DX5+NKT cells are able to prevent colitis induced by CD4+CD62Lhigh T lymphocytes in a SCID mouse model. The aim of this study was to further investigate the underlying mechanism in vitro.
Methods: CD4+CD62Lhigh and DX5+NKT cells from the spleen of Balb/c mice were isolated first by MACS, followed by FACS sorting and cocultured for up to 96 h. After polyclonal stimulation with anti-CD3, anti-CD28, and IL-2, proliferation of CD4+CD62Lhigh cells was assessed using a CFSE assay and activity of proapoptotic caspase-3 was determined by intracellular staining and flow cytometry. Extrinsic apoptotic pathway was blocked using an unconjugated antibody against FasL, and activation of caspase-3 was measured.
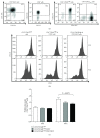
Results: As previously shown in vivo, DX5+NKT cells inhibit proliferation of CD4+CD62Lhigh cells in vitro after 96 h coculture compared to a CD4+CD62Lhigh monoculture (proliferation index: 1.39 ± 0.07 vs. 1.76 ± 0.12; P = 0.0079). The antiproliferative effect of DX5+NKT cells was likely due to an induction of apoptosis in CD4+CD62Lhigh cells as evidenced by increased activation of the proapoptotic caspase-3 after 48 h (38 ± 3% vs. 28 ± 3%; P = 0.0451). Furthermore, DX5+NKT cells after polyclonal stimulation showed an upregulation of FasL on their cell surface (15 ± 2% vs. 2 ± 1%; P = 0.0286). Finally, FasL was blocked on DX5+NKT cells, and therefore, the extrinsic apoptotic pathway abrogated the activation of caspase-3 in CD4+CD62Lhigh cells.
Conclusion: Collectively, these data confirmed that DX5+NKT cells inhibit proliferation of colitis-inducing CD4+CD62Lhigh cells by induction of apoptosis. Furthermore, DX5+NKT cells likely mediate their cytotoxic and proapoptotic potentials via FasL, confirming recent reports about iNKT cells. Further studies will be necessary to evaluate the therapeutical potential of these immunoregulatory cells in patients with colitis.
Figures




Similar articles
-
DX5+ NKT cells induce the death of colitis-associated cells: involvement of programmed death ligand-1.Eur J Immunol. 2006 May;36(5):1210-21. doi: 10.1002/eji.200535332. Eur J Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16619286
-
Migration and chemokine receptor pattern of colitis-preventing DX5+NKT cells.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011 Nov;26(11):1423-33. doi: 10.1007/s00384-011-1249-x. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2011. PMID: 21647599
-
A new model of chronic colitis in SCID mice induced by adoptive transfer of CD62L+ CD4+ T cells: insights into the regulatory role of interleukin-6 on apoptosis.Pathobiology. 2002-2003;70(3):170-6. doi: 10.1159/000068150. Pathobiology. 2002. PMID: 12571422
-
DX5+NKT cells display phenotypical and functional differences between spleen and liver as well as NK1.1-Balb/c and NK1.1+ C57Bl/6 mice.BMC Immunol. 2011 Apr 29;12:26. doi: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-26. BMC Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21529347 Free PMC article.
-
The majority of lamina propria CD4(+) T-cells from scid mice with colitis undergo Fas-mediated apoptosis in vivo.Immunol Lett. 2001 Aug 1;78(1):7-12. doi: 10.1016/s0165-2478(01)00240-1. Immunol Lett. 2001. PMID: 11470145
Cited by
-
PD-1+ CD4 T cell immune response is mediated by HIF-1α/NFATc1 pathway after P. yoelii infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 24;13:942862. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.942862. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36091043 Free PMC article.
-
Ikzf2 Regulates the Development of ICOS+ Th Cells to Mediate Immune Response in the Spleen of S. japonicum-Infected C57BL/6 Mice.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 12;12:687919. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.687919. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34475870 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

