Antiapoptotic Molecule Survivin in Transplantation: Helpful or Harmful?
- PMID: 30364092
- PMCID: PMC6188762
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/6492034
Antiapoptotic Molecule Survivin in Transplantation: Helpful or Harmful?
Abstract
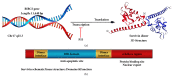
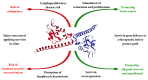
Survivin, an antiapoptotic molecule from inhibitor of apoptosis protein (IAP) family, is most known for its implication in cancer as there are some efforts to apply it for diagnostic as well as therapeutic purposes in oncology. On the other hand, it could be a useful molecule to be positively targeted when trying to save tissue and promote cells viability. Since protecting the allograft from ischemia reperfusion injury and inflammation-induced damage is a considerable objective in transplantation, it is reasonable to take advantage from antiapoptotic agents like survivin in order to achieve this goal. However, survivin's potential ability to induce malignancies makes some concerns about its use in clinic. The other barrier is this molecule's involvement in lymphocytes development and proliferation which might increase the risk of graft rejection due to adaptive immune system overactivation. In this review we summarize the few studies carried out about survivin's effect on graft survival and probable advantages and disadvantages of its overexpression in transplantation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Old Flame Never Dies: Survivin in Cancer and Cellular Senescence.Gerontology. 2016;62(2):173-81. doi: 10.1159/000432398. Epub 2015 Jul 3. Gerontology. 2016. PMID: 26159786 Review.
-
Overexpression of survivin in pediatric Hodgkin lymphoma tumor cells: Characterization of protein expression and splice-variants transcription profile.Exp Mol Pathol. 2019 Jun;108:24-31. doi: 10.1016/j.yexmp.2019.03.005. Epub 2019 Mar 12. Exp Mol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 30876863
-
The inhibitor of apoptosis protein survivin is associated with high-risk behavior of neuroblastoma.J Pediatr Surg. 2001 Dec;36(12):1785-91. doi: 10.1053/jpsu.2001.28839. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. PMID: 11733907
-
Functional characterization of novel mutations affecting survivin (BIRC5)-mediated therapy resistance in head and neck cancer patients.Hum Mutat. 2013 Feb;34(2):395-404. doi: 10.1002/humu.22249. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Hum Mutat. 2013. PMID: 23161837
-
Survivin study: what is the next wave?J Cell Physiol. 2003 Oct;197(1):8-29. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10327. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 12942537 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of anti - Apoptotic survivin in odontogenic keratocyst, adenomatoid odontogenic tumor and ameloblastoma.J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2023 Jul-Sep;27(3):601. doi: 10.4103/jomfp.jomfp_446_22. Epub 2023 Sep 12. J Oral Maxillofac Pathol. 2023. PMID: 38033952 Free PMC article.
-
The Apoptosis Inhibitor Protein Survivin Is a Critical Cytoprotective Resistor against Silica-Based Nanotoxicity.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023 Sep 12;13(18):2546. doi: 10.3390/nano13182546. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37764575 Free PMC article.
-
Managing allorejection in off-the-shelf CAR-engineered cell therapies.Mol Ther. 2025 Jun 4;33(6):2368-2390. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.11.035. Epub 2024 Nov 26. Mol Ther. 2025. PMID: 39600090 Review.
-
Effects of ginsenoside Rb1 on spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 Aug 14;14(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1299-2. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019. PMID: 31412899 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altieri D. C., Marchisio C. Survivin apoptosis: An interloper between cell death and cell proliferation in cancer. Laboratory Investigation. 1999;79(11):1327–1333. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

