Randomized Clinical Trial to Assess the Impact of the Broadly Neutralizing HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibody VRC01 on HIV-1 Persistence in Individuals on Effective ART
- PMID: 30364428
- PMCID: PMC6195652
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofy242
Randomized Clinical Trial to Assess the Impact of the Broadly Neutralizing HIV-1 Monoclonal Antibody VRC01 on HIV-1 Persistence in Individuals on Effective ART
Abstract
Background: Broadly neutralizing monoclonal antibodies (bnMAbs) may promote clearance of HIV-1-expressing cells through antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. We evaluated the effect of the CD4-binding site bnMAb, VRC01, on measures of HIV-1 persistence in chronically infected individuals.
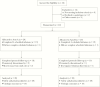
Methods: A5342 was a phase 1, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm study. Participants on effective antiretroviral therapy (ART) were randomized to receive 2 infusions of VRC01 (40 mg/kg) at entry and week 3, and 2 infusions of placebo (saline) at weeks 6 and 9; or 2 infusions of placebo at entry and week 3, and 2 infusions of VRC01 at weeks 6 and 9.
Results: Infusion of VRC01 was safe and well tolerated. The median fold-change in the cell-associated HIV-1 RNA/DNA ratio from baseline to week 6 was 1.12 and 0.83 for the VRC01 and placebo arms, respectively, with no significant difference between arms (P = .16). There were no significant differences in the proportions with residual plasma viremia ≥1 copies/mL or in phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate/ionomycin-induced virus production from CD4+ T cells between arms (both P > .05).
Conclusions: In individuals with chronic HIV-1 infection on ART, VRC01 infusions were safe and well tolerated but did not affect plasma viremia, cellular HIV-1 RNA/DNA levels, or stimulated virus production from CD4+ T cells.
Clinicaltrialsgov identifier: NCT02411539.
Keywords: HIV-1 cure; HIV-1 persistence; VRC01; bnMAb; clinical trial.
Figures
References
-
- Finzi D, Blankson J, Siliciano JD, et al. Latent infection of CD4+ T cells provides a mechanism for lifelong persistence of HIV-1, even in patients on effective combination therapy. Nat Med 1999; 5:512–7. - PubMed
-
- Ferrari G, Pollara J, Kozink D, et al. An HIV-1 gp120 envelope human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a C1 conformational epitope mediates potent antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) activity and defines a common ADCC epitope in human HIV-1 serum. J Virol 2011; 85:7029–36. - PMC - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069511/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069439/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001857/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001079/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050410/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI094189/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069494/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069465/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068619/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001082/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069503/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002243/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- K23 CA177321/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001070/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI027757/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials