Hearing treatment for reducing cognitive decline: Design and methods of the Aging and Cognitive Health Evaluation in Elders randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 30364572
- PMCID: PMC6197326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trci.2018.08.007
Hearing treatment for reducing cognitive decline: Design and methods of the Aging and Cognitive Health Evaluation in Elders randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Introduction: Hearing impairment is highly prevalent and independently associated with cognitive decline. The Aging and Cognitive Health Evaluation in Elders study is a multicenter randomized controlled trial to determine efficacy of hearing treatment in reducing cognitive decline in older adults. Clinicaltrials.gov Identifier: NCT03243422.
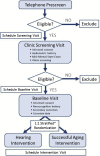
Methods: Eight hundred fifty participants without dementia aged 70 to 84 years with mild-to-moderate hearing impairment recruited from four United States field sites and randomized 1:1 to a best-practices hearing intervention or health education control. Primary study outcome is 3-year change in global cognitive function. Secondary outcomes include domain-specific cognitive decline, incident dementia, brain structural changes on magnetic resonance imaging, health-related quality of life, physical and social function, and physical activity.
Results: Trial enrollment began January 4, 2018 and is ongoing.
Discussion: When completed in 2022, Aging and Cognitive Health Evaluation in Elders study should provide definitive evidence of the effect of hearing treatment versus education control on cognitive decline in community-dwelling older adults with mild-to-moderate hearing impairment.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Cognition; Dementia; Epidemiology; Hearing; Longitudinal study; Memory; Presbycusis.
Figures
References
-
- Livingston G., Sommerlad A., Orgeta V., Costafreda S.G., Huntley J., Ames D. Dementia prevention, intervention, and care. Lancet. 2017;390:2673–2734. - PubMed
Associated data
Grants and funding
- HHSN268201100009I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096812/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG049638/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG023291/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG055426/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005G/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096917/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R34 AG046548/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096814/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG054693/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL070825/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL096899/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical