Database Resources of the BIG Data Center in 2019
- PMID: 30365034
- PMCID: PMC6323991
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gky993
Database Resources of the BIG Data Center in 2019
Abstract
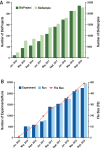
The BIG Data Center at Beijing Institute of Genomics (BIG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences provides a suite of database resources in support of worldwide research activities in both academia and industry. With the vast amounts of multi-omics data generated at unprecedented scales and rates, the BIG Data Center is continually expanding, updating and enriching its core database resources through big data integration and value-added curation. Resources with significant updates in the past year include BioProject (a biological project library), BioSample (a biological sample library), Genome Sequence Archive (GSA, a data repository for archiving raw sequence reads), Genome Warehouse (GWH, a centralized resource housing genome-scale data), Genome Variation Map (GVM, a public repository of genome variations), Science Wikis (a catalog of biological knowledge wikis for community annotations) and IC4R (Information Commons for Rice). Newly released resources include EWAS Atlas (a knowledgebase of epigenome-wide association studies), iDog (an integrated omics data resource for dog) and RNA editing resources (for editome-disease associations and plant RNA editosome, respectively). To promote biodiversity and health big data sharing around the world, the Open Biodiversity and Health Big Data (BHBD) initiative is introduced. All of these resources are publicly accessible at http://bigd.big.ac.cn.
Figures
References
-
- Guo L., Winzer T., Yang X., Li Y., Ning Z., He Z., Teodor R., Lu Y., Bowser T.A., Graham I.A. et al. The opium poppy genome and morphinan production. Science. 2018; doi: 10.1126/science.aat4096. - PubMed

