Betulinic acid inhibits stemness and EMT of pancreatic cancer cells via activation of AMPK signaling
- PMID: 30365057
- PMCID: PMC6254859
- DOI: 10.3892/ijo.2018.4604
Betulinic acid inhibits stemness and EMT of pancreatic cancer cells via activation of AMPK signaling
Abstract
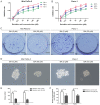
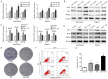
Cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are found in various types of human cancer, including pancreatic cancer, possess elevated metastatic potential, lead to tumor recurrence and cause chemoradiotherapy resistance. Alterations in cellular bioenergetics through the regulation of 5' adenosine monophosphate‑activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling may be a prerequisite to stemness. Betulinic acid (BA) is a well‑known bioactive compound with antiretroviral and anti‑inflammatory potential, which has been reported to exert anticancer effects on various types of cancer, including pancreatic cancer. The present study aimed to investigate whether BA could inhibit pancreatic CSCs via regulation of AMPK signaling. The proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells was examined by MTT and colony formation assays. The migratory and invasive abilities of pancreatic cancer cells were assessed using wound‑scratch and Transwell invasion assays. In addition, the expression levels of candidate genes were measured by reverse transcription‑quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. The results revealed that BA inhibited the proliferation and tumorsphere formation of pancreatic cancer cells, suppressed epithelial‑mesenchymal transition (EMT), migration and invasion, and reduced the expression of three pluripotency factors [SRY‑box 2 (Sox2), octamer‑binding protein 4 (Oct4) and Nanog]. Furthermore, immunohistochemical analysis confirmed that there was a significant inverse association between the expression levels of phosphorylated (P)‑AMPK and Sox2 in pancreatic cancer, and it was revealed that BA may activate AMPK signaling. Notably, knockdown of AMPK reversed the suppressive effects of BA on EMT and stemness of pancreatic cancer cells. In addition, BA reversed the effects of gemcitabine on stemness and enhanced the sensitivity of pancreatic cancer cells to gemcitabine. Collectively, these results indicated that BA may effectively inhibit pluripotency factor expression (Sox2, Oct4 and Nanog), EMT and the stem‑like phenotype of pancreatic cancer cells via activating AMPK signaling. Therefore, BA may be considered an attractive therapeutic candidate and an effective inhibitor of the stem‑like phenotype in pancreatic cancer cells. Further investigation into the development of BA as an anticancer drug is warranted.
Keywords: betulinic acid; pancreatic cancer; cancer stem cells; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; 5' adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase; gemcitabine.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

