Spikeling: A low-cost hardware implementation of a spiking neuron for neuroscience teaching and outreach
- PMID: 30365493
- PMCID: PMC6221365
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2006760
Spikeling: A low-cost hardware implementation of a spiking neuron for neuroscience teaching and outreach
Abstract
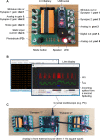
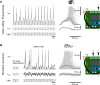
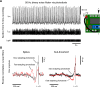
Understanding how neurons encode and compute information is fundamental to our study of the brain, but opportunities for hands-on experience with neurophysiological techniques on live neurons are scarce in science education. Here, we present Spikeling, an open source in silico implementation of a spiking neuron that costs £25 and mimics a wide range of neuronal behaviours for classroom education and public neuroscience outreach. Spikeling is based on an Arduino microcontroller running the computationally efficient Izhikevich model of a spiking neuron. The microcontroller is connected to input ports that simulate synaptic excitation or inhibition, to dials controlling current injection and noise levels, to a photodiode that makes Spikeling light sensitive, and to a light-emitting diode (LED) and speaker that allows spikes to be seen and heard. Output ports provide access to variables such as membrane potential for recording in experiments or digital signals that can be used to excite other connected Spikelings. These features allow for the intuitive exploration of the function of neurons and networks mimicking electrophysiological experiments. We also report our experience of using Spikeling as a teaching tool for undergraduate and graduate neuroscience education in Nigeria and the United Kingdom.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Vectorized algorithms for spiking neural network simulation.Neural Comput. 2011 Jun;23(6):1503-35. doi: 10.1162/NECO_a_00123. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Neural Comput. 2011. PMID: 21395437
-
Persistent spiking activity in neuromorphic circuits incorporating post-inhibitory rebound excitation.J Neural Eng. 2024 Jun 20;21(3). doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad56c8. J Neural Eng. 2024. PMID: 38861961
-
Constructing Precisely Computing Networks with Biophysical Spiking Neurons.J Neurosci. 2015 Jul 15;35(28):10112-34. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4951-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26180189 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of facts and issues about neural coding by spikes.J Physiol Paris. 2010 Jan-Mar;104(1-2):5-18. doi: 10.1016/j.jphysparis.2009.11.002. Epub 2009 Nov 29. J Physiol Paris. 2010. PMID: 19925865 Review.
-
A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: II. Inhomogeneous synaptic input and network properties.Biol Cybern. 2006 Aug;95(2):97-112. doi: 10.1007/s00422-006-0082-8. Epub 2006 Jul 5. Biol Cybern. 2006. PMID: 16821035 Review.
Cited by
-
Spiking Neuron Mathematical Models: A Compact Overview.Bioengineering (Basel). 2023 Jan 29;10(2):174. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering10020174. Bioengineering (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36829668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Think: Theory for Africa.PLoS Comput Biol. 2019 Jul 11;15(7):e1007049. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007049. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Comput Biol. 2019. PMID: 31295253 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Using Open Neuroscience to Advance Equity in the Pedagogy and Research Infrastructure in Colleges/Universities Still Financially Impacted by COVID-19: The Emergence of a Global Resource Network Aimed at Integrating Neuroscience and Society.J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2023 May 19;21(2):E2-E7. doi: 10.59390/JVIC5712. eCollection 2023 Spring. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2023. PMID: 37588641 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Neurosimilator for Undergraduate Biophysics and Neurophysiology Courses.J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2024 Aug 31;22(3):A207-A216. doi: 10.59390/MIUV3158. eCollection 2024 Spring. J Undergrad Neurosci Educ. 2024. PMID: 39355677 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

