Proteome and microbiota analysis reveals alterations of liver-gut axis under different stocking density of Peking ducks
- PMID: 30365498
- PMCID: PMC6203259
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198985
Proteome and microbiota analysis reveals alterations of liver-gut axis under different stocking density of Peking ducks
Abstract
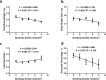
This study aimed to determine the impact of stocking density on the liver proteome and cecal microbiota of Peking ducks. A total of 1,200 21-day-old ducks were randomly assigned to 5 stocking density groups of 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 ducks/m2, with 6 replicates for each group. At 40 days of age, duck serum and pectorals were collected for biochemical tests; liver and cecal contents of ducks were gathered for proteome and microbiota analysis, respectively. Serum MDA increased while pectorals T-AOC reduced linearly with enhancing stocking density. Duck lipid metabolism was altered under different stocking density as well. Serum LDL-C increased linearly with increasing stocking density. Proteome analysis revealed fatty acid biosynthesis proteins such as acyl-CoA synthetase family member 2 and fatty acid oxidation related proteins including acyl-CoA dehydrogenase long chain and acyl-coenzyme A oxidase were enriched in high stocking density group. Additionally, high stocking density increased oxidative response associated proteins such as DDRGK domain containing 1. Furthermore, increasing stocking density diminished proteins of anti-oxidant capacity including regucalcin and catalase. 16S rDNA analysis revealed that higher stocking density was accompanied with decreased microbial diversity, as well as depletion of anti-inflammatory bacterial taxa, including Bacteroidales, Butyricimonas and Alistipe. Besides, reduced bile acid metabolism-associated bacteria such as Ruminococcaceae, Clostridiales and Desulfovibrionaceae were found in the high-density group. Both proteome and 16S rDNA results showed inflammation and chronic liver disease trend in the high-density group, which suggests the involvement of the liver-gut axis in oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Impact of stocking densities on growth, organ index, serum biochemistry, gut morphology and microbiota of young ducks in a rice-duck-crayfish coculture system.Anim Biosci. 2025 May;38(5):1067-1080. doi: 10.5713/ab.24.0488. Epub 2025 Jan 24. Anim Biosci. 2025. PMID: 39901714 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of curcumin on ochratoxin A-induced liver oxidative injury in duck is mediated by modulating lipid metabolism and the intestinal microbiota.Poult Sci. 2020 Feb;99(2):1124-1134. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.041. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32036964 Free PMC article.
-
Severe riboflavin deficiency induces alterations in the hepatic proteome of starter Pekin ducks.Br J Nutr. 2017 Nov;118(9):641-650. doi: 10.1017/S0007114517002641. Br J Nutr. 2017. PMID: 29185933
-
Global waterfowl production: stocking rate is a key factor for improving productivity and well-being-a review.Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023 Nov 24;55(6):419. doi: 10.1007/s11250-023-03835-6. Trop Anim Health Prod. 2023. PMID: 37996713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fatty acid metabolism and acyl-CoA synthetases in the liver-gut axis.World J Hepatol. 2021 Nov 27;13(11):1512-1533. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1512. World J Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34904027 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Metabolome and Microbiota Analysis Reveals the Conducive Effect of Pediococcus acidilactici BCC-1 and Xylan Oligosaccharides on Broiler Chickens.Front Microbiol. 2021 May 28;12:683905. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.683905. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34122394 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ultrasound-induced stress on gut microbiota of mice.Vet World. 2023 May;16(5):929-938. doi: 10.14202/vetworld.2023.929-938. Epub 2023 May 7. Vet World. 2023. PMID: 37576770 Free PMC article.
-
Growth, carcass parameters, biochemical and oxidative stress indices, and meat traits of duck breeds under different stocking densities.Poult Sci. 2022 Sep;101(9):101992. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101992. Epub 2022 Jun 5. Poult Sci. 2022. PMID: 35841644 Free PMC article.
-
Microbiota, Gut Health and Chicken Productivity: What Is the Connection?Microorganisms. 2019 Sep 20;7(10):374. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7100374. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31547108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of nicotinamide and sodium butyrate on meat quality and muscle ubiquitination degradation genes in broilers reared at a high stocking density.Poult Sci. 2020 Mar;99(3):1462-1470. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2019.10.070. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32115032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buijs S, Keeling LJ, Vangestel C, Baert J, Vangeyte J, Tuyttens FAM (2010) Resting or hiding? Why broiler chickens stay near walls and how density affects this. Appl Anim Behav Sci 124: 97–103.
-
- Simitzis PE, Kalogeraki E, Goliomytis M, Charismiadou MA, Triantaphyllopoulos K, Ayoutanti A, et al. (2012) Impact of stocking density on broiler growth performance, meat characteristics, behavioural components and indicators of physiological and oxidative stress. Br Poult Sci 53: 721–730. 10.1080/00071668.2012.745930 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

