Acute blood pressure responses after different isometric handgrip protocols in hypertensive patients
- PMID: 30365821
- PMCID: PMC6172980
- DOI: 10.6061/clinics/2018/e373
Acute blood pressure responses after different isometric handgrip protocols in hypertensive patients
Abstract
Objective: The present study analyzed blood pressure responses after a single session of isometric handgrip exercise performed with different volumes and intensities by patients with hypertension.
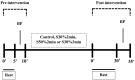
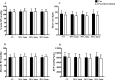
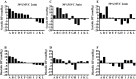
Methods: This randomized crossover trial submitted 12 hypertensive patients (58±5 years old) to four isometric handgrip exercise sessions in a random order: 4 x 2 min at 30% of the maximal voluntary contraction (S30%); 4 x 2 min at 50% of the maximal voluntary contraction (S50%2min); 4 x 3 min at 30% of the maximal voluntary contraction (S30%3min); and a control session. The systolic and diastolic blood pressure, heart rate, and rate-pressure product were measured pre- and post-exercise (30th min).
Results: No significant changes were observed in cardiovascular variables after any session (p>0.05 for all comparisons). Similarly, individual analyses revealed heterogeneity in the responses, including increases in blood pressure observed in some sessions. Patients with reduced blood pressure after an isometric handgrip exercise session exhibited a higher body mass index, diastolic blood pressure and heart rate (p<0.05). They also tended to be younger (p=0.07).
Conclusion: Isometric handgrip exercise performed with different intensities and volumes did not reduce the blood pressure of hypertensive patients.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global status report on noncommunicable diseases 2010. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2011.
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R. Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;14;360((9349)):1903–13. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Badrov MB, Bartol CL, DiBartolomeo MA, Millar PJ, McNevin NH, McGowan CL. Effects of isometric handgrip training dose on resting blood pressure and resistance vessel endothelial function in normotensive women. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113((8)):2091–100. doi: 10.1007/s00421-013-2644-5. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

