Tart Cherry Reduces Inflammation in Adipose Tissue of Zucker Fatty Rats and Cultured 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
- PMID: 30366378
- PMCID: PMC6266132
- DOI: 10.3390/nu10111576
Tart Cherry Reduces Inflammation in Adipose Tissue of Zucker Fatty Rats and Cultured 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Abstract
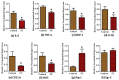
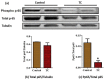
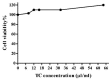
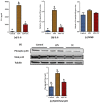
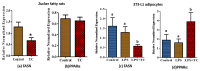
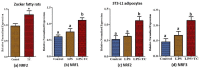
Obesity increases adipose tissue inflammation and secretion of pro-inflammatory adipokines, which have systemic effects on the organism's health status. Our objective was to dissect mechanisms of anti-inflammatory effects of tart cherry (TC) in adipose tissue of Zucker fatty rats, and cultured 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Rats were fed either a control diet, or 4% TC powder diets for eight weeks. Body and epididymal fat pad weights were not significantly different between control and TC groups. However, rats fed the TC diet had significantly reduced adipose tissue inflammation (p < 0.05), as determined by reduced mRNA levels of pro-inflammatory markers including interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), interleukin-1beta (IL-1β), monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 (MCP-1), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and CD-11b, and increased mRNA levels of type-1 arginase (Arg-1) anti-inflammatory marker. Consistent with these in vivo results, TC significantly decreased expression of IL-6 mRNA and protein levels in lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulated adipocytes compared to those stimulated with LPS, but no TC. Moreover, both in vivo (rat adipose tissue) and in vitro (3T3-L1 adipocytes), phosphorylation of p65-NF-κB subunit was significantly reduced by TC. Additionally, TC decreased mRNA expression of fatty acid synthase (FASN), and increased expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARα), master regulator of lipid oxidation, and anti-oxidant markers nuclear factor erythroid-derived 2-related factor (NRFs) in both models. In conclusion, our findings indicate that TC downregulates inflammation in part via the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) pathway in adipose tissue. Thus, TC may serve as a potential intervention to reduce obesity-associated inflammation.
Keywords: adipose tissue; inflammation; obesity; tart cherry.
Conflict of interest statement
S.J., A.M., S.S., J.H.K., K.C.-L. and N.M.-M. declare no conflict of interest. TC was a gift from the Cherry Marketing Institute to K.C.-L. and N.M.-M., A.J.S. received research funds from the Cherry Marketing Institute (CMI) for the animal study; however, CMI had no role or involvement in any part of this research.
Figures



References
-
- Word Health Organization Obesity and Overweight. [(accessed on 8 August 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs311/en/
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

