Small Molecule Optoacoustic Contrast Agents: An Unexplored Avenue for Enhancing In Vivo Imaging
- PMID: 30366395
- PMCID: PMC6278390
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23112766
Small Molecule Optoacoustic Contrast Agents: An Unexplored Avenue for Enhancing In Vivo Imaging
Abstract
Almost every variety of medical imaging technique relies heavily on exogenous contrast agents to generate high-resolution images of biological structures. Organic small molecule contrast agents, in particular, are well suited for biomedical imaging applications due to their favorable biocompatibility and amenability to structural modification. PET/SPECT, MRI, and fluorescence imaging all have a large host of small molecule contrast agents developed for them, and there exists an academic understanding of how these compounds can be developed. Optoacoustic imaging is a relatively newer imaging technique and, as such, lacks well-established small molecule contrast agents; many of the contrast agents used are the same ones which have found use in fluorescence imaging applications. Many commonly-used fluorescent dyes have found successful application in optoacoustic imaging, but others generate no detectable signal. Moreover, the structural features that either enable a molecule to generate a detectable optoacoustic signal or prevent it from doing so are poorly understood, so design of new contrast agents lacks direction. This review aims to compile the small molecule optoacoustic contrast agents that have been successfully employed in the literature to bridge the information gap between molecular design and optoacoustic signal generation. The information contained within will help to provide direction for the future synthesis of optoacoustic contrast agents.
Keywords: contrast agents; near-infrared; optoacoustic; small molecule.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

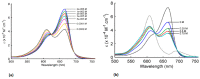
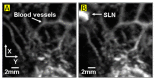



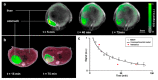
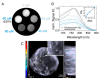

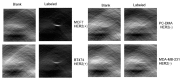


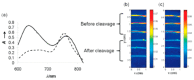

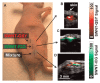

References
-
- Ntziachristos V., Schellenberger E.A., Ripoll J., Yessayan D., Graves E., Bogdanov A., Josephson L., Weissleder R. Visualization of antitumor treatment by means of fluorescence molecular tomography with an annexin V-Cy5.5 conjugate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:12294–12299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0401137101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

