Aptamers and Aptasensors for Highly Specific Recognition and Sensitive Detection of Marine Biotoxins: Recent Advances and Perspectives
- PMID: 30366456
- PMCID: PMC6265707
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins10110427
Aptamers and Aptasensors for Highly Specific Recognition and Sensitive Detection of Marine Biotoxins: Recent Advances and Perspectives
Abstract
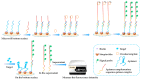
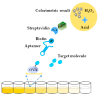
Marine biotoxins distribute widely, have high toxicity, and can be easily accumulated in water or seafood, exposing a serious threat to consumer health. Achieving specific and sensitive detection is the most effective way to prevent emergent issues caused by marine biotoxins; however, the previous detection methods cannot meet the requirements because of ethical or technical drawbacks. Aptamers, a kind of novel recognition element with high affinity and specificity, can be used to fabricate various aptasensors (aptamer-based biosensors) for sensitive and rapid detection. In recent years, an increasing number of aptamers and aptasensors have greatly promoted the development of marine biotoxins detection. In this review, we summarized the recent aptamer-related advances for marine biotoxins detection and discussed their perspectives. Firstly, we summarized the sequences, selection methods, affinity, secondary structures, and the ion conditions of all aptamers to provide a database-like information; secondly, we summarized the reported aptasensors for marine biotoxins, including principles, detection sensitivity, linear detection range, etc.; thirdly, on the basis of the existing reports and our own research experience, we forecast the development prospects of aptamers and aptasensors for marine biotoxins detection. We hope this review not only provides a comprehensive summary of aptamer selection and aptasensor development for marine biotoxins, but also arouses a broad readership amongst academic researchers and industrial chemists.
Keywords: aptamer; aptasensor; food safety; marine biotoxin; rapid detection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

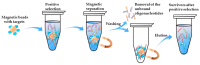
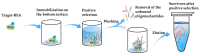
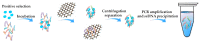
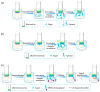

References
-
- Turner A.D., Higgins C., Davidson K., Veszelovszki A., Payne D., Hungerford J., Higman W. Potential threats posed by new or emerging marine biotoxins in UK waters and examination of detection methodology used in their control: Brevetoxins. Mar. Drugs. 2015;13:1224–1254. doi: 10.3390/md13031224. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rodríguez I., Vieytes M.R., Alfonso A. Analytical challenges for regulated marine toxins. Detection methods. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017;18:29–36. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2017.10.008. - DOI
-
- Alsabi A., Mcarthur J., Ostroumov V., French R.J. Marine toxins that target voltage-gated sodium channels. Mar. Drugs. 2006;4:157–192. doi: 10.3390/md403157. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

