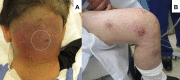
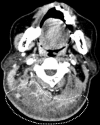
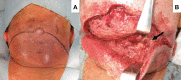
Neck carbuncle associated with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia
- PMID: 30366898
- PMCID: PMC6203058
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2018-226935
Neck carbuncle associated with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia
Keywords: head and neck surgery; infections; skin.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus arrives in Hong Kong.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004 Oct;54(4):845-6. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkh426. Epub 2004 Sep 8. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2004. PMID: 15355941 No abstract available.
-
Bone and joint infection as a predictor of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia: a comparative cohort study.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014 Jul;69(7):1966-71. doi: 10.1093/jac/dku076. Epub 2014 Apr 2. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2014. PMID: 24695351
-
Emergence of multidrug-resistant sequence type 45 strains among mecA-positive borderline oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus causing bacteraemia in a medical centre in Taiwan.Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018 Jul;52(1):70-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.02.014. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018. PMID: 29505885
-
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia and pneumonia.Dis Mon. 2008 Dec;54(12):787-92. doi: 10.1016/j.disamonth.2008.09.008. Dis Mon. 2008. PMID: 18996281 Review. No abstract available.
-
Mandatory surveillance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) bacteraemia in England: the first 10 years.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012 Apr;67(4):802-9. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr561. Epub 2012 Jan 4. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012. PMID: 22223229 Review.
References
-
- O’Dell ML. Skin and wound infections: an overview. Am Fam Physician 1998;57:2424–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
