Genus-Wide Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance in Lactobacillus spp
- PMID: 30366997
- PMCID: PMC6293106
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.01738-18
Genus-Wide Assessment of Antibiotic Resistance in Lactobacillus spp
Abstract
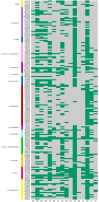
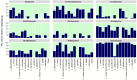
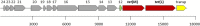
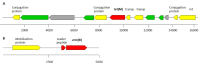
Lactobacillus species are widely used as probiotics and starter cultures for a variety of foods, supported by a long history of safe usage. Although more than 35 species meet the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) criteria for qualified presumption of safety status, the safety of Lactobacillus species and their carriage of antibiotic resistance (AR) genes is under continuing ad hoc review. To comprehensively update the identification of AR in the genus Lactobacillus, we determined the antibiotic susceptibility patterns of 182 Lactobacillus type strains and compared these phenotypes to their genotypes based on genome-wide annotations of AR genes. Resistances to trimethoprim, vancomycin, and kanamycin were the most common phenotypes. A combination of homology-based screening and manual annotation identified genes encoding resistance to aminoglycosides (20 sequences), tetracycline (18), erythromycin (6), clindamycin (60), and chloramphenicol (42). In particular, the genes aac(3) and lsa, involved in resistance to aminoglycosides and clindamycin, respectively, were found in Lactobacillus spp. Acquired determinants predicted to code for tetracycline and erythromycin resistance were detected in Lactobacillus ingluviei, Lactobacillus amylophilus, and Lactobacillus amylotrophicus, flanked in the genome by mobile genetic elements with potential for horizontal transfer.IMPORTANCELactobacillus species are generally considered to be nonpathogenic and are used in a wide variety of foods and products for humans and animals. However, many of the species examined in this study have antibiotic resistance levels which exceed those recommended by the EFSA, suggesting that these cutoff values should be reexamined in light of the genetic basis for resistance discussed here. Our data provide evidence for rationally revising the regulatory guidelines for safety assessment of lactobacilli entering the food chain as starter cultures, food preservatives, or probiotics and will facilitate comprehensive genotype-based assessment of strains for safety screening.
Keywords: Lactobacillus; antimicrobial resistance; genomics.
Copyright © 2018 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Characterization of Antibiotic Resistance Genes from Lactobacillus Isolated from Traditional Dairy Products.J Food Sci. 2017 Mar;82(3):724-730. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13645. Epub 2017 Feb 9. J Food Sci. 2017. PMID: 28182844
-
Characterization of antimicrobial resistance in lactobacilli and bifidobacteria used as probiotics or starter cultures based on integration of phenotypic and in silico data.Int J Food Microbiol. 2020 Feb 2;314:108388. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108388. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Int J Food Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 31707173
-
Antibiotic resistance of Lactobacillus pentosus and Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides isolated from naturally-fermented Aloreña table olives throughout fermentation process.Int J Food Microbiol. 2014 Feb 17;172:110-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2013.11.025. Epub 2013 Dec 3. Int J Food Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24370969
-
Antibiotic resistance and virulence factors in lactobacilli: something to carefully consider.Food Microbiol. 2022 May;103:103934. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2021.103934. Epub 2021 Nov 8. Food Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35082060 Review.
-
Antibiotic resistance in food lactic acid bacteria--a review.Int J Food Microbiol. 2005 Dec 15;105(3):281-95. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2005.03.008. Epub 2005 Nov 8. Int J Food Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16289406 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic Susceptibility, Resistance Gene Determinants and Corresponding Genomic Regions in Lactobacillus amylovorus Isolates Derived from Wild Boars and Domestic Pigs.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 30;11(1):103. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11010103. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36677394 Free PMC article.
-
Hybridization alters the gut microbial and metabolic profile concurrent with modifying intestinal functions in Tunchang pigs.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 20;14:1159653. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1159653. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37152756 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoglycemic, Antioxidant Activities, and Probiotic Characteristics of Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LBUX2302 Isolated from Stool Samples of Neonates.Life (Basel). 2025 May 18;15(5):804. doi: 10.3390/life15050804. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40430230 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic bacteria of wild boar origin intended for piglets - An in vitro study.Vet Med (Praha). 2024 Aug 29;69(8):281-296. doi: 10.17221/35/2024-VETMED. eCollection 2024 Aug. Vet Med (Praha). 2024. PMID: 39296628 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular identification and antibiotic resistance of bacteriocinogenic lactic acid bacteria isolated from table olives.Arch Microbiol. 2021 Mar;203(2):597-607. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-02053-0. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Arch Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 32995979
References
-
- Berendonk TU, Manaia CM, Merlin C, Fatta-Kassinos D, Cytryn E, Walsh F, Bürgmann H, Sørum H, Norström M, Pons MN, Kreuzinger N, Huovinen P, Stefani S, Schwartz T, Kisand V, Baquero F, Martinez JL. 2015. Tackling antibiotic resistance: the environmental framework. Nat Rev Microbiol 13:310–317. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3439. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

