Gynura Rhizoma containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids induces the hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in mice via upregulating fibrosis-related factors
- PMID: 30367152
- PMCID: PMC6786394
- DOI: 10.1038/s41401-018-0155-y
Gynura Rhizoma containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids induces the hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in mice via upregulating fibrosis-related factors
Abstract
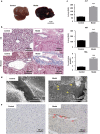
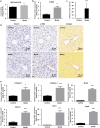
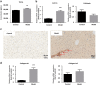
Recently, hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (HSOS) caused by herbal preparations containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs), such as Gynura Rhizoma (Tusanqi), has gained global attention. However, the lack of a reliable and reproducible animal model has greatly hampered mechanistic studies. Therefore, we aimed to establish a reproducible HSOS mouse model and investigate the hepatotoxic mechanism. The model was established by intragastrical administration of Gynura Rhizoma extract, i.e., 1.0 g extract/kg per day (equal to 16.7 g crude drug/kg per day based on extraction rate and 49.1 mg PA/kg per day based on the total PA content in the extract determined) for 40 successive days. Then, the mice were sacrificed, and their blood samples and livers were collected for analyses. Using hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and Masson staining, scanning electron microscopy imaging, clinical biomarkers, and other assays, we showed that the HSOS was successfully induced in our mouse model. Furthermore, we detected the key factors involved in liver fibrosis in the mice, revealing significantly increased hydroxyproline concentration; elevated expression of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and fibrosis-related genes such as Collagen-1, Collagen-3, Mmp2, Mmp13, Timp1, Timp3, and Activin, upregulated Smad3 phosphorylation, and increased serum TGF-β levels. Moreover, pro-inflammatory cytokines, including Tnf-α, Il-1β, and Il-6, were also increased in the model. All these results demonstrate the key roles of the TGF-β-Smad3 and inflammatory signaling pathways in this Gynura Rhizoma-induced HSOS mouse model, suggesting that blockade of fibrosis and/or inflammation should be an effective treatment for HSOS.
Keywords: Gynura Rhizoma; hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome; herbal-induced liver injury; inflammation; liver fibrosis; pyrrolizidine alkaloid.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
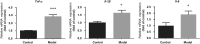
Similar articles
-
The long persistence of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-derived pyrrole-protein adducts in vivo: Kinetic study following multiple exposures of a pyrrolizidine alkaloid containing extract of Gynura japonica.Toxicol Lett. 2020 May 1;323:41-47. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2020.01.021. Epub 2020 Jan 23. Toxicol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31982501
-
Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated with consumption of Gynura segetum.J Hepatol. 2011 Apr;54(4):666-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2010.07.031. Epub 2010 Sep 22. J Hepatol. 2011. PMID: 21146894 Review.
-
First evidence of pyrrolizidine alkaloid N-oxide-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome in humans.Arch Toxicol. 2017 Dec;91(12):3913-3925. doi: 10.1007/s00204-017-2013-y. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Arch Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 28620673
-
Tusanqi and hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.J Dig Dis. 2014 Mar;15(3):105-7. doi: 10.1111/1751-2980.12112. J Dig Dis. 2014. PMID: 24528632 Review.
-
Characterization of liver injury induced by a pyrrolizidine alkaloid in rats.Phytomedicine. 2021 Aug;89:153595. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153595. Epub 2021 May 16. Phytomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34153877
Cited by
-
Comparison of chloroplast genomes of Gynura species: sequence variation, genome rearrangement and divergence studies.BMC Genomics. 2019 Oct 29;20(1):791. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-6196-x. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31664913 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical Profiling, Acute Toxicity, and Hepatoprotective Effects of Anchusa Limbata in Thioacetamide-Induced Liver Cirrhosis in Rats.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Nov 21;12(12):10628-10645. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4544. eCollection 2024 Dec. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39723071 Free PMC article.
-
Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for the treatment of hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome caused by pyrrolizidine alkaloids: A multicenter retrospective study.Heliyon. 2023 Dec 8;10(1):e23455. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e23455. eCollection 2024 Jan 15. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38163189 Free PMC article.
-
A TMT-based shotgun proteomics uncovers overexpression of thrombospondin 1 as a contributor in pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Jul;96(7):2003-2019. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03281-7. Epub 2022 Mar 31. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35357534 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Genus Gynura: A Systematic Review.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 27;11:504624. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.504624. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33328981 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

