Sequence characterization of the 5S ribosomal DNA and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region in four European Donax species (Bivalvia: Donacidae)
- PMID: 30367592
- PMCID: PMC6204057
- DOI: 10.1186/s12863-018-0684-x
Sequence characterization of the 5S ribosomal DNA and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) region in four European Donax species (Bivalvia: Donacidae)
Abstract
Background: The whole repeat unit of 5S rDNA and the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) of four European Donax species were analysed. After amplifying, cloning and sequencing several 5S and ITS units, their basic features and their variation were described. The phylogenetic usefulness of 5S and ITS sequences in the inference of evolutionary relationships among these wedge clams was also investigated.
Results: The length of the 5S repeat presented little variation among species, except D. trunculus that differed from the rest of the Donax species in 170-210 bp. The deduced coding region covered 120 bp, and showed recognizable internal control regions (ICRs) involved in the transcription. The length of non-transcribed spacer region (NTS) ranged from 157 bp to 165 bp in Donax trunculus and from 335 bp to 367 bp in the other three species. The conservation degree of transcriptional regulatory regions was analysed revealing a conserved TATA-like box in the upstream region. Regarding ITS sequences, the four Donax species showed slight size differences among clones due to the variation occurring in the ITS1 and ITS2, except Donax variegatus did not display size differences in the ITS2. The total length of the ITS sequence ranged between 814 and 1014 bp. Resulting phylogenetic trees display that the two ribosomal DNA regions provide well-resolved phylogenies where the four European Donax species form a single clade receiving high support in nodes. The topology obtained with 5S sequences was in agreement with Donax evolutionary relationships inferred from several sequences of different nature in previous studies.
Conclusions: This is not only a basic research work, where new data and new knowledge is provided about Donax species, but also have allowed the authentication of these wedge clams and offers future applications to provide other genetic resources.
Keywords: 5S unit; Donax; Internal transcribed spacer; Ribosomal DNA; Wedge clams.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Compliance with ethical standards. Field work was conducted in accordance with local legislation and with regulations and guidelines established by the University of A Coruña. No endangered or protected species were involved.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

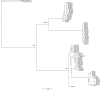
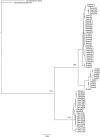
References
-
- Bejega García V, González Gómez de Agüero E, Fernández Rodríguez C, Álvarez García JC (2010) Los concheros de O Neixón (Boiro, A Coruña) y Punta Atalaia (San Cibrao, Lugo): Una propuesta de muestreo y excavación de depósitos de la Edad del Hierro y época romana en Galicia, en González Gómez de Agüero, E., Bejega García, V., Fernández Rodríguez, C. y Prieto Fuertes, N. (coord.), Actas de la I Reunión de Arqueomalacología de la Península Ibérica. Spain: Férvedes. 33–42.
-
- Bogenhagen DF, Brown DD. Nucleotide sequences in Xenopus 5S DNA required for transcription terminator. Cell. 1981;24(1):261–270. - PubMed
-
- Cheng HL, Meng XP, Ji HJ, Dong ZG, Chen SY. Sequence analysis of the ribosomal DNA internal transcribed and 5.8S ribosomal RNA gene in representatives of the clam family Veneridae (Mollusca: Bivalvia) J Shellfish Res. 2006;25(3):833–839.
-
- Chícharo L, Chícharo A, Gaspar M, Alves F, Regala J. Ecological characterization of dredged and non-dredged bivalve fishing areas off South Portugal. J Mar Biol Assoc UK. 2002;82:41–50.
-
- Chow S, Ueno Y, Toyokawa M, Oohara I, Takeyama H. Preliminary analysis of length and GC content variation in the ribosomal first internal transcribed spacer (ITS1) of marine animals. Mar Biotechnol. 2009;11(3):301–306. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

