Reproducible bioinformatics project: a community for reproducible bioinformatics analysis pipelines
- PMID: 30367595
- PMCID: PMC6191970
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-018-2296-x
Reproducible bioinformatics project: a community for reproducible bioinformatics analysis pipelines
Abstract
Background: Reproducibility of a research is a key element in the modern science and it is mandatory for any industrial application. It represents the ability of replicating an experiment independently by the location and the operator. Therefore, a study can be considered reproducible only if all used data are available and the exploited computational analysis workflow is clearly described. However, today for reproducing a complex bioinformatics analysis, the raw data and the list of tools used in the workflow could be not enough to guarantee the reproducibility of the results obtained. Indeed, different releases of the same tools and/or of the system libraries (exploited by such tools) might lead to sneaky reproducibility issues.
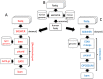
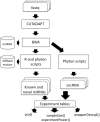
Results: To address this challenge, we established the Reproducible Bioinformatics Project (RBP), which is a non-profit and open-source project, whose aim is to provide a schema and an infrastructure, based on docker images and R package, to provide reproducible results in Bioinformatics. One or more Docker images are then defined for a workflow (typically one for each task), while the workflow implementation is handled via R-functions embedded in a package available at github repository. Thus, a bioinformatician participating to the project has firstly to integrate her/his workflow modules into Docker image(s) exploiting an Ubuntu docker image developed ad hoc by RPB to make easier this task. Secondly, the workflow implementation must be realized in R according to an R-skeleton function made available by RPB to guarantee homogeneity and reusability among different RPB functions. Moreover she/he has to provide the R vignette explaining the package functionality together with an example dataset which can be used to improve the user confidence in the workflow utilization.
Conclusions: Reproducible Bioinformatics Project provides a general schema and an infrastructure to distribute robust and reproducible workflows. Thus, it guarantees to final users the ability to repeat consistently any analysis independently by the used UNIX-like architecture.
Keywords: Chromatin Immuno precipitation sequencing; Community; Docker; Reproducible research; Single nucleotide variants; Whole transcriptome sequencing; microRNA sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Building Containerized Workflows Using the BioDepot-Workflow-Builder.Cell Syst. 2019 Nov 27;9(5):508-514.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.cels.2019.08.007. Epub 2019 Sep 11. Cell Syst. 2019. PMID: 31521606 Free PMC article.
-
Bioportainer Workbench: a versatile and user-friendly system that integrates implementation, management, and use of bioinformatics resources in Docker environments.Gigascience. 2019 Apr 1;8(4):giz041. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz041. Gigascience. 2019. PMID: 31222200 Free PMC article.
-
CREDO: a friendly Customizable, REproducible, DOcker file generator for bioinformatics applications.BMC Bioinformatics. 2024 Mar 12;25(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s12859-024-05695-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2024. PMID: 38475691 Free PMC article.
-
A bioinformatics workflow to decipher transcriptomic data from vitamin D studies.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019 May;189:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.01.003. Epub 2019 Feb 1. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30716464 Review.
-
Reproducible, scalable, and shareable analysis pipelines with bioinformatics workflow managers.Nat Methods. 2021 Oct;18(10):1161-1168. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01254-9. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 34556866 Review.
Cited by
-
rCASC: reproducible classification analysis of single-cell sequencing data.Gigascience. 2019 Sep 1;8(9):giz105. doi: 10.1093/gigascience/giz105. Gigascience. 2019. PMID: 31494672 Free PMC article.
-
EAVLD 2024 - 7th Congress of the European Association of Veterinary Laboratory Diagnosticians.Ital J Food Saf. 2024 Dec 16;13(4):13488. doi: 10.4081/ijfs.2024.13488. eCollection 2024 Nov 12. Ital J Food Saf. 2024. PMID: 39829721 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicle miRNome during subclinical mastitis in dairy cows.Vet Res. 2024 Sep 19;55(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13567-024-01367-x. Vet Res. 2024. PMID: 39300590 Free PMC article.
-
Nonproteolytic ubiquitination regulates chromatin occupancy by the NCoR/SMRT/HDAC3 corepressor complex in MCF-7 breast cancer cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 May 6;122(18):e2502805122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2502805122. Epub 2025 Apr 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 40305047 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma microRNAs as potential biomarkers in early Alzheimer disease expression.Sci Rep. 2022 Sep 16;12(1):15589. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-19862-6. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36114255 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

