Clinicopathological and prognostic correlations of HER3 expression and its degradation regulators, NEDD4-1 and NRDP1, in primary breast cancer
- PMID: 30367623
- PMCID: PMC6204010
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-018-4917-1
Clinicopathological and prognostic correlations of HER3 expression and its degradation regulators, NEDD4-1 and NRDP1, in primary breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Human epidermal growth factor receptor HER3 (ErbB3), especially in association with its relative HER2 (ErbB2), is known as a key oncogene in breast tumour biology. Nonetheless, the prognostic relevance of HER3 remains controversial. NEDD4-1 and NRDP1 are signalling molecules closely related to the degradation of HER3 via ubiquitination. NEDD4-1 and NRDP1 have been reported to contribute to HER3-mediated signalling by regulating its localization and cell membrane retention. We studied correlations between HER3, NEDD4-1, and NRDP1 protein expression and their association with tumour histopathological characteristics and clinical outcomes.
Methods: The prevalence of immunohistochemically detectable expression profiles of HER3 (n = 177), NEDD4-1 (n = 145), and NRDP1 (n = 145) proteins was studied in primary breast carcinomas on archival formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) samples. Clinicopathological correlations were determined statistically using Pearson's Chi-Square test. The Kaplan-Meier method, log-rank test (Mantel-Cox), and Cox regression analysis were utilized for survival analysis.
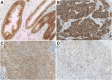
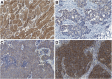
Results: HER3 protein was expressed in breast carcinomas without association with HER2 gene amplification status. Absence or low HER3 expression correlated with clinically aggressive features, such as triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) phenotype, basal cell origin (cytokeratin 5/14 expression combined with ER negativity), large tumour size, and positive lymph node status. Low total HER3 expression was prognostic for shorter recurrence-free survival time in HER2-amplified breast cancer (p = 0.004, p = 0.020 in univariate and multivariate analyses, respectively). The majority (82.8%) of breast cancers demonstrated NEDD4-1 protein expression - while only a minor proportion (8.3%) of carcinomas expressed NRDP1. NEDD4-1 and NRDP1 expression were not associated with clinical outcomes in HER2-amplified breast cancer, irrespective of adjuvant trastuzumab therapy.
Conclusions: Low HER3 expression is suggested to be a valuable prognostic biomarker to predict recurrence in HER2-amplified breast cancer. Neither NEDD4-1 nor NRDP1 demonstrated relevance in prognostics or in the subclassification of HER2-amplified breast carcinomas.
Keywords: Breast cancer; ErbB3; FLRF; HER3; NEDD4–1; NRDP1; Prognostic biomarker; RNF41; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The use of the tumour samples and patient records in this study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Pirkanmaa Hospital District (references no. R07082, R00143), the Ministry of Social Affairs and Health, and the National Authority for Medicolegal Affairs in Finland. The need for informed consent was waived by the aforementioned authorities due to the large number of samples and the fact that a sizeable portion of the patients were already deceased. Individual patient data has not been made available and the dataset has been handled anonymized.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
None of the authors declares any conflicts of interest.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
NEDD4 expression is associated with breast cancer progression and is predictive of a poor prognosis.Breast Cancer Res. 2019 Dec 19;21(1):148. doi: 10.1186/s13058-019-1236-7. Breast Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31856858 Free PMC article.
-
Nrdp1 expression to predict clinical outcome and efficacy of adjuvant anthracyclines-based chemotherapy in breast cancer: A retrospective study.Cancer Biomark. 2015;15(2):115-23. doi: 10.3233/CBM-140443. Cancer Biomark. 2015. PMID: 25519010
-
Loss of Nrdp1 enhances ErbB2/ErbB3-dependent breast tumor cell growth.Cancer Res. 2006 Dec 1;66(23):11279-86. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-2319. Cancer Res. 2006. PMID: 17145873
-
ERBB3/HER3 and ERBB2/HER2 duet in mammary development and breast cancer.J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008 Jun;13(2):215-23. doi: 10.1007/s10911-008-9083-7. Epub 2008 May 3. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18454306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of ERBB3/HER3 signaling in cancer.Oncotarget. 2014 Nov 15;5(21):10222-36. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.2655. Oncotarget. 2014. PMID: 25400118 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PI3K and MAPK Pathways as Targets for Combination with the Pan-HER Irreversible Inhibitor Neratinib in HER2-Positive Breast Cancer and TNBC by Kinome RNAi Screening.Biomedicines. 2021 Jun 28;9(7):740. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070740. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34203351 Free PMC article.
-
Expression and regulatory network of E3 ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 family in cancers.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 8;23(1):526. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11007-w. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37291499 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the Potential Role of NEDD4-like E3 Ligases in Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Oct 16;23(20):12380. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012380. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36293239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy: What's new in 2023?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023 Apr-May;27(4-5):305-324. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2023.2218613. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2023. PMID: 37243489 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring novel therapeutic targets in small bowel adenocarcinoma: insights from claudin 18.2, nectin-4, and HER3 expression analysis.ESMO Open. 2025 Jan;10(1):104098. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2024.104098. Epub 2025 Jan 3. ESMO Open. 2025. PMID: 39754977 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang N, Chang Y, Rios A, An Z. HER3/ErbB3, an emerging cancer therapeutic target. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin Shanghai. 2016;48(1):39–48. - PubMed
-
- Berger MB, Mendrola JM, Lemmon MA. ErbB3/HER3 does not homodimerize upon neuregulin binding at the cell surface. FEBS Lett. 2004;569(1–3):332–336. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

