Peptide vaccine against chikungunya virus: immuno-informatics combined with molecular docking approach
- PMID: 30368237
- PMCID: PMC6204282
- DOI: 10.1186/s12967-018-1672-7
Peptide vaccine against chikungunya virus: immuno-informatics combined with molecular docking approach
Abstract
Background: Chikungunya virus (CHIKV), causes massive outbreaks of chikungunya infection in several regions of Asia, Africa and Central/South America. Being positive sense RNA virus, CHIKV replication within the host resulting in its genome mutation and led to difficulties in creation of vaccine, drugs and treatment strategies. Vector control strategy has been a gold standard to combat spreading of CHIKV infection, but to eradicate a species from the face of earth is not an easy task. Therefore, alongside vector control, there is a dire need to prevent the infection through vaccine as well as through antiviral strategies.
Methods: This study was designed to find out conserved B cell and T cell epitopes of CHIKV structural proteins through immuno-informatics and computational approaches, which may play an important role in evoking the immune responses against CHIKV.
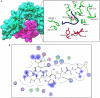
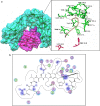
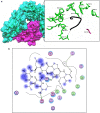
Results: Several conserved cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitopes, linear and conformational B cell epitopes were predicted for CHIKV structural polyprotein and their antigenicity was calculated. Among B-cell epitopes "PPFGAGRPGQFGDI" showed a high antigenicity score and it may be highly immunogenic. In case of T cell epitopes, MHC class I peptides 'TAECKDKNL' and MHC class II peptides 'VRYKCNCGG' were found extremely antigenic.
Conclusion: The study led to the discovery of various epitopes, conserved among various strains belonging to different countries. The potential antigenic epitopes can be successfully utilized in designing novel vaccines for combating and eradication of CHIKV disease.
Keywords: B cell and T cell epitopes; Chikungunya virus (CHIKV); Computational approaches; Vaccine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epitope-based peptide vaccine design and target site depiction against Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus: an immune-informatics study.J Transl Med. 2019 Nov 8;17(1):362. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-2116-8. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31703698 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of Epitope-Based Peptide Vaccine Against the Chikungunya Virus by Immuno-informatics Approach.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(4):325-340. doi: 10.2174/1389201020666191112161743. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 31721709
-
In silico analysis of MHC-I restricted epitopes of Chikungunya virus proteins: Implication in understanding anti-CHIKV CD8(+) T cell response and advancement of epitope based immunotherapy for CHIKV infection.Infect Genet Evol. 2015 Apr;31:118-26. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2015.01.017. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Infect Genet Evol. 2015. PMID: 25643869
-
Peptide-based vaccinology: experimental and computational approaches to target hypervariable viruses through the fine characterization of protective epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibodies and the identification of T-cell-activating peptides.Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:521231. doi: 10.1155/2013/521231. Epub 2013 Jun 26. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23878584 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Brief Review of Computer-Assisted Approaches to Rational Design of Peptide Vaccines.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 4;17(5):666. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050666. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27153063 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
mRNA Vaccine Designing Using Chikungunya Virus E Glycoprotein through Immunoinformatics-Guided Approaches.Vaccines (Basel). 2022 Sep 6;10(9):1476. doi: 10.3390/vaccines10091476. Vaccines (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36146554 Free PMC article.
-
Immunoinformatics Approach to Design Multi-Epitope- Subunit Vaccine against Bovine Ephemeral Fever Disease.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;9(8):925. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9080925. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34452050 Free PMC article.
-
A Review: The Antiviral Activity of Cyclic Peptides.Int J Pept Res Ther. 2023;29(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s10989-022-10478-y. Epub 2022 Dec 1. Int J Pept Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36471676 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study of combining virtual screening and antiviral treatments of the Sars-CoV-2 (Covid-19).Microb Pathog. 2020 Sep;146:104241. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2020.104241. Epub 2020 May 5. Microb Pathog. 2020. PMID: 32387389 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural basis of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro and anti-COVID-19 drug discovery from medicinal plants.J Pharm Anal. 2020 Aug;10(4):313-319. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2020.03.009. Epub 2020 Mar 26. J Pharm Anal. 2020. PMID: 32296570 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

