Recognizing Brain States Using Deep Sparse Recurrent Neural Network
- PMID: 30369441
- PMCID: PMC6508593
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2018.2877576
Recognizing Brain States Using Deep Sparse Recurrent Neural Network
Abstract
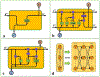
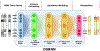
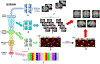
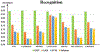
Brain activity is a dynamic combination of different sensory responses and thus brain activity/state is continuously changing over time. However, the brain's dynamical functional states recognition at fast time-scales in task fMRI data have been rarely explored. In this paper, we propose a novel 5-layer deep sparse recurrent neural network (DSRNN) model to accurately recognize the brain states across the whole scan session. Specifically, the DSRNN model includes an input layer, one fully-connected layer, two recurrent layers, and a softmax output layer. The proposed framework has been tested on seven task fMRI data sets of Human Connectome Project. Extensive experiment results demonstrate that the proposed DSRNN model can accurately identify the brain's state in different task fMRI data sets and significantly outperforms other auto-correlation methods or non-temporal approaches in the dynamic brain state recognition accuracy. In general, the proposed DSRNN offers a new methodology for basic neuroscience and clinical research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identifying Brain Networks at Multiple Time Scales via Deep Recurrent Neural Network.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019 Nov;23(6):2515-2525. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2882885. Epub 2018 Nov 22. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2019. PMID: 30475739 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiable neural architecture search for optimal spatial/temporal brain function network decomposition.Med Image Anal. 2021 Apr;69:101974. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.101974. Epub 2021 Jan 20. Med Image Anal. 2021. PMID: 33588118
-
Deep neural networks and kernel regression achieve comparable accuracies for functional connectivity prediction of behavior and demographics.Neuroimage. 2020 Feb 1;206:116276. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116276. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Neuroimage. 2020. PMID: 31610298 Free PMC article.
-
Spatio-temporal modeling of connectome-scale brain network interactions via time-evolving graphs.Neuroimage. 2018 Oct 15;180(Pt B):350-369. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.10.067. Epub 2017 Nov 10. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 29102809 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bayesian networks for fMRI: a primer.Neuroimage. 2014 Feb 1;86:573-82. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.10.020. Epub 2013 Oct 18. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 24140939 Review.
Cited by
-
Attention module improves both performance and interpretability of four-dimensional functional magnetic resonance imaging decoding neural network.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Jun 1;43(8):2683-2692. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25813. Epub 2022 Feb 25. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35212436 Free PMC article.
-
A Noise-Robust Framework for Automatic Segmentation of COVID-19 Pneumonia Lesions From CT Images.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020 Aug;39(8):2653-2663. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2020.3000314. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32730215 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling task-based fMRI data via deep belief network with neural architecture search.Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2020 Jul;83:101747. doi: 10.1016/j.compmedimag.2020.101747. Epub 2020 Jun 6. Comput Med Imaging Graph. 2020. PMID: 32593949 Free PMC article.
-
Simultaneous spatial-temporal decomposition for connectome-scale brain networks by deep sparse recurrent auto-encoder.Brain Imaging Behav. 2021 Oct;15(5):2646-2660. doi: 10.1007/s11682-021-00469-w. Epub 2021 Mar 23. Brain Imaging Behav. 2021. PMID: 33755922
-
ACTION: Augmentation and computation toolbox for brain network analysis with functional MRI.Neuroimage. 2025 Jan;305:120967. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2024.120967. Epub 2024 Dec 21. Neuroimage. 2025. PMID: 39716522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Friston KJ, Holmes AP, Worsley KJ, Poline JP, Frith CD, and Frackowiak RSJ, Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: A general linear approach, HUM BRAIN MAPP, vol. 2, (no. 4), pp. 189–210, 1994.
-
- Lv J, Jiang X, Li X, Zhu D, Chen H, Zhang T, Zhang S, Hu X, Han J, and Huang H, Sparse Representation of Whole-brain FMRI Signals for Identification of Functional Networks, MED IMAGE ANAL, vol. 20, (no. 1), pp. 112–134, 2014. - PubMed
-
- Zhao S, Han J, Lv J, Jiang X, Hu X, Zhao Y, Ge B, Guo L, and Liu T, Supervised Dictionary Learning for Inferring Concurrent Brain Networks., IEEET MED IMAGING, vol. 34, (no. 10), pp. 2036, 2015. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

