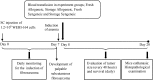
Immunomodulatory Effects of Blood Transfusion on Tumor Size, Metastasis, and Survival in Experimental Fibrosarcoma
- PMID: 30369743
- PMCID: PMC6186234
- DOI: 10.1007/s12288-018-0962-9
Immunomodulatory Effects of Blood Transfusion on Tumor Size, Metastasis, and Survival in Experimental Fibrosarcoma
Abstract
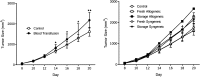
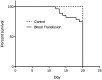
In spite of efforts, blood transfusion is still accompanied with adverse effects such as transfusion-related immunomodulation (TRIM). The current study aimed to evaluate the effects of allogeneic, syngeneic, fresh and storage blood transfusion on the growth and metastasis of tumors and survival in fibrosarcoma bearing BALB/c mice. Twenty-five BALB/c mice were grouped into five groups of equal size. All groups were injected 1.2 × 106 WEHI-164 cells subcutaneously to induce fibrosarcoma tumor. After expansion of the tumor, in four groups (except for the control group), hemorrhage-induced anemia was developed. Twenty-four hours later, blood deficit was replaced by fresh allogeneic, storage allogeneic, fresh syngeneic and storage syngeneic blood transfusion, respectively. After a blood transfusion, for 13 days, the tumor size and survival of the mice were evaluated. In the day 20, the mice were sacrificed and their spleen tissues were evaluated for TRIM induced metastasis. Tumor size increase in the groups that received allogeneic (fresh and storage) and storage syngeneic blood transfusion was significantly higher than the control group (P value < 0.05). However, no significant difference was present in survival between the experiment groups and the control group. There was no metastasis in none of groups at the end of the study. Allogeneic and storage blood transfusion could have immunomodulatory effects such as increased tumor size. However, it seems that fresh and syngeneic blood transfusion have no effects on tumor growth in fibrosarcoma bearing mice. Further evidence may prove that more attention is warranted in blood transfusion into cancer cases.
Keywords: Blood transfusion; Fibrosarcoma; Immunomodulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Tarbiat Modares University.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources