Quantitative Approaches to Assess Key Carcinogenic Events of Genotoxic Carcinogens
- PMID: 30370003
- PMCID: PMC6195881
- DOI: 10.5487/TR.2018.34.4.291
Quantitative Approaches to Assess Key Carcinogenic Events of Genotoxic Carcinogens
Abstract
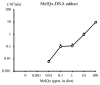
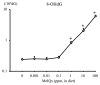
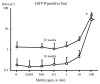
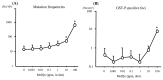
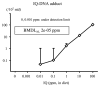
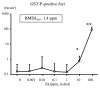
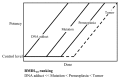
Chemical carcinogenesis is a multistep process. Genotoxic carcinogens, which are DNA-reactive, induce DNA adduct formation and genetic alterations in target cells, thereby generating mutated cells (initiation). Subsequently, preneoplastic lesions appear through clonal proliferation of the mutated cells and transform into tumors (promotion and progression). Many factors may influence these processes in a dose-dependent manner. Therefore, quantitative analysis plays an important role in studies on the carcinogenic threshold of genotoxic carcinogens. Herein, we present data on the relationship between key carcinogenic events and their deriving point of departure (PoD). Their PoDs were also compared to those of the carcinogenesis pathway. In an experiment, the liver of rats exposed to 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-(4,5-f)quinoxaline (MeIQx) was examined to determine the formation of MeIQx-DNA adducts, generation of mutations at LacI transgene, and induction of preneoplastic glutathione S-transferase placental form (GST-P)-positive foci and tumors (benign and malignant). The PoDs of the above key events in the carcinogenicity of MeIQx were increased as the carcinogenesis advanced; however, these PoDs were lower than those of tumor induction. Thus, the order of key events during tumor induction in the liver was as follows: formation of DNA adducts << Mutations << GST-positive foci (preneoplasia) << Tumor (adenoma and carcinoma). We also obtained similar data on the genotoxic and carcinogenic PoDs of other hepatocarcinogens, such as 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo(4,5-f)quinoline. These results contribute to elucidating the existence of a genotoxic and carcinogenic threshold.
Keywords: Cancer risk assessment; Genotoxic carcinogen; IQ; Linear no-threshold carcinogenicity; MeIQx; Point of departure.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST There are no financial or other interests regarding the submitted manuscript that might be construed as a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Qualitative and quantitative approaches in the dose-response assessment of genotoxic carcinogens.Mutagenesis. 2016 May;31(3):341-6. doi: 10.1093/mutage/gev049. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Mutagenesis. 2016. PMID: 26152227 Review.
-
Lack of Hepatocarcinogenicity of Combinations of Low Doses of 2-amino-3, 8-dimethylimidazo[4,5- f ]quinoxaline and Diethylnitrosamine in Rats: Indication for the Existence of a Threshold for Genotoxic Carcinogens.J Toxicol Pathol. 2012 Sep;25(3):209-14. doi: 10.1293/tox.25.209. Epub 2012 Oct 1. J Toxicol Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22988339 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence of a threshold-effect for 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-[4,5-f]quinoxaline liver carcinogenicity in F344/DuCrj rats.Toxicol Pathol. 2008 Apr;36(3):472-7. doi: 10.1177/0192623308315671. Epub 2008 Apr 15. Toxicol Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18413788
-
Effects of chronic administration of low doses of 2-amino-3,8-dimethylimidazo-[4,5-f]quinoxaline on glutathione S-transferase placental form-positive foci development in the livers of rats fed a choline-deficient diet.Jpn J Cancer Res. 1993 Aug;84(8):859-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1993.tb02058.x. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1993. PMID: 8407550 Free PMC article.
-
Value of GST-P positive preneoplastic hepatic foci in dose-response studies of hepatocarcinogenesis: evidence for practical thresholds with both genotoxic and nongenotoxic carcinogens. A review of recent work.Toxicol Pathol. 2003 Jan-Feb;31(1):80-6. doi: 10.1080/01926230390173879. Toxicol Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12597451 Review.
Cited by
-
Konzept für die Bewertung von krebserzeugenden Stoffen im bevölkerungsbezogenen Human-Biomonitoring – Stellungnahme der Kommission Human-Biomonitoring des Umweltbundesamtes.Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022 Sep;65(9):951-957. doi: 10.1007/s00103-022-03570-7. Bundesgesundheitsblatt Gesundheitsforschung Gesundheitsschutz. 2022. PMID: 36048212 German. No abstract available.
-
Rationale and Roadmap for Developing Panels of Hotspot Cancer Driver Gene Mutations as Biomarkers of Cancer Risk.Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020 Jan;61(1):152-175. doi: 10.1002/em.22326. Epub 2019 Oct 6. Environ Mol Mutagen. 2020. PMID: 31469467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concept for the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Substances in Population-Based Human Biomonitoring.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Jun 13;19(12):7235. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19127235. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35742488 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Farmer JH, Kodell RL, Greenman DL, Shaw GW. Dose and time responses models for the incidence of bladder and liver neoplasms in mice fed 2-acetylaminofluorene continuously. J Environ Pathol Toxicol. 1980;3:55–68. - PubMed
-
- Peto R, Gray R, Brantom P, Grasso P. Effects on 4080 rats of chronic ingestion of N-nitrosodiethylamine or N-nitrosodimethylamine: a detailed dose-response study. Cancer Res. 1991;51:6415–6451. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

