Biomarker Profiling in Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Identifies the Relationship between Angiopoietin-2 and Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 30370780
- PMCID: PMC6707900
- DOI: 10.1177/1076029618808909
Biomarker Profiling in Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Identifies the Relationship between Angiopoietin-2 and Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
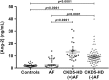
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is prevalent in nearly 27% of patients with stage 5 chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis (CKD5-HD), suggesting a strong association between these 2 pathologies. It is hypothesized that the relationship between these 2 diseases may be mediated by inflammation. Angiopoietin-2 (Ang-2), a pro-inflammatory biomarker of endothelial instability, inflammation, and vascular remodeling, is elevated in CKD5-HD and AF, yet has not been evaluated in patients with concomitant AF and CKD5-HD. The aim of this study is to analyze circulating levels of inflammatory and thrombotic biomarkers in patients with concomitant AF and CKD5-HD. Plasma levels of Ang-2 were measured via sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay method in CKD5-HD patients (n = 96), patients with AF (n = 38), and controls (n = 50). Angiopoietin-2 was markedly elevated in CKD5-HD with comorbid AF as compared to CKD5-HD alone, and AF alone, respectively (13.05 ± 1.56 vs 9.57 ± 0.71 ng/mL; P = .00169; vs 2.48 ± 0.57 ng/mL; P < .0001). The results of this study suggest an additive effect of Ang-2 with coexistence of AF and CKD5-HD, which may be useful in the detection of AF within this patient population.
Keywords: angiopoietin-2; atrial fibrillation; biomarkers; chronic kidney disease; hemodialysis; inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Procalcitonin as a Marker of Comorbid Atrial Fibrillation in Chronic Kidney Disease and History of Sepsis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020 Jan-Dec;26:1076029620932228. doi: 10.1177/1076029620932228. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32539447 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated extracellular nucleosomes and their relevance to inflammation in stage 5 chronic kidney disease.Int Angiol. 2018 Oct;37(5):419-426. doi: 10.23736/S0392-9590.18.03987-1. Epub 2018 Apr 11. Int Angiol. 2018. PMID: 29644836 Free PMC article.
-
Biomarkers of Endothelial, Renal, and Platelet Dysfunction in Stage 5 Chronic Kidney Disease Hemodialysis Patients With Heart Failure.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018 Mar;24(2):235-240. doi: 10.1177/1076029617729216. Epub 2017 Oct 8. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2018. PMID: 28990414 Free PMC article.
-
Inflammatory Biomarkers in Atrial Fibrillation.Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(5):837-854. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170727103357. Curr Med Chem. 2019. PMID: 28748764 Review.
-
MicroRNAs: Emerging biomarkers for atrial fibrillation.J Cardiol. 2019 Dec;74(6):475-482. doi: 10.1016/j.jjcc.2019.05.018. Epub 2019 Jul 16. J Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31324570 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring Angiopoietin-2: Clinical Insights and Experimental Perspectives in Kidney Diseases.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Sep 6;9(12):3375-3385. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.09.001. eCollection 2024 Dec. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39698365 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Procalcitonin as a Marker of Comorbid Atrial Fibrillation in Chronic Kidney Disease and History of Sepsis.Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020 Jan-Dec;26:1076029620932228. doi: 10.1177/1076029620932228. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2020. PMID: 32539447 Free PMC article.
-
The association of coagulation and atrial fibrillation: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Europace. 2023 Feb 8;25(1):28-39. doi: 10.1093/europace/euac130. Europace. 2023. PMID: 35942591 Free PMC article.
-
Myocardial Oedema as a Consequence of Viral Infection and Persistence-A Narrative Review with Focus on COVID-19 and Post COVID Sequelae.Viruses. 2024 Jan 14;16(1):121. doi: 10.3390/v16010121. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38257821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarker-based prediction of sinus rhythm in atrial fibrillation patients: the EAST-AFNET 4 biomolecule study.Eur Heart J. 2024 Dec 16;45(47):5002-5019. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae611. Eur Heart J. 2024. PMID: 39215973 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Genovesi S, Pogliani D, Faini A, et al. Prevalence of atrial fibrillation and associated factors in a population of long-term hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2005;46(5):897–902. - PubMed
-
- Watanabe H, Watanabe T, Sasaki S, Nagai K, Roden DM, Aizawa Y. Close bidirectional relationship between chronic kidney disease and atrial fibrillation: the Niigata preventive medicine study. Am Heart J. 2009;158(4):629–636. - PubMed
-
- Vazquez E, Sanchez-Perales C, Garcia-Garcia F, et al. Atrial fibrillation in incident dialysis patients. Kidney Int. 2009;76(3):324–330. - PubMed
-
- Genovesi S, Vincenti A, Rossi E, et al. Atrial fibrillation and morbidity and mortality in a cohort of long-term hemodialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008;51(2):255–262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

