Treatment of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Dyes in Wastewater by Grafted Titania Pillared Clay Membranes
- PMID: 30370870
- PMCID: PMC6327120
- DOI: 10.2174/1872210512666181029155352
Treatment of Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange Dyes in Wastewater by Grafted Titania Pillared Clay Membranes
Abstract
Background: Amphoteric membranes such as Titania Pillared Clay (TiPILC) membranes exhibit different charges at different pH ranges, subsequently show efficient separation for cationic and anionic organic pollutants in wastewater based on solution pH. The structural properties of such membranes determine their permeability and selectivity to a large extent. The present work is initiated to explore the possibility of enhancing the surface area of TiPILC membranes by grafting with 3- aminopropyltriethoxysilane.
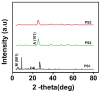
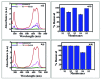
Method: Grafted TiPILC membranes were fabricated by colloidal sol- gel route followed by dip coating, drying and sintering the membranes at 300°C. X-ray diffraction (XRD) spectra of the pillared photocatalyst membranes show the presence of only anatase phase, which exhibits better photocatalytic activity. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) spectra reveal the formation of delaminated TiPILC material. The specific surface area of TiPILC membrane obtained at pH3.5 is 183m2/g.
Results: Literature survey of 47 papers was carried out for the work. 10 papers were based on patents being dealt on degradation of organic dyes in wastewater by conventional methods, though reports of membrane technology are limited in literature. The rest 37 papers outlined the importance of widespread use of titania photocatalyst powder for degradation studies.
Conclusion: The membrane material thus developed is efficient in complete decolouration of both Methylene Blue and Methyl Orange dyes on account of the high surface charge and high surface area in just one cycle of filtration.
Keywords: Titania pillared clay membranes; adsorption; amphoteric; dye degradation; grafting; low cost; photocatalysis; separation; wastewater..
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.net.
Figures






References
-
- Yuan L., Huang D., Guo W., Yang Q., Yu J. TiO2/montmorillonite nanocomposite for removal of organic pollutant. Appl. Clay Sci. 2011;53:272–278.
-
- Rauf M.A., Meetani M.A., Khaleel A., Ahmed A. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue using a mixed catalyst and product analysis by LC/MS. Chem. Eng. J. 2010;157:373–378.
-
- Lucaci D., Duta A. Adsorption of methyl orange from wastewater using sawdust and sawdust fly ash substrates. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2011;10(9):1255–1262.
-
- Zhang Y., Wang D., Zhang G. Photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants by TiO2/sepiolite composites prepared at low temperature. Chem. Eng. J. 2011;173:1–10.
-
- Cao X., Oda Y., Sirashi F. Photocatalytic and adsorptive treatment of 2, 4-dinitrophenol using a TiO2 film covering activated C surface. Chem. Eng. J. 2010;156:98–105.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

