Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Cancer: A Danish Population-Based Cohort Study
- PMID: 30371150
- PMCID: PMC6201425
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009543
Atrial Fibrillation and Risk of Cancer: A Danish Population-Based Cohort Study
Abstract
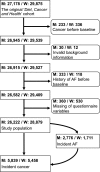
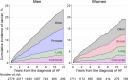
Background Atrial fibrillation ( AF ) and cancer are frequent diseases worldwide. The timewise association between the diagnosis of AF and a subsequent diagnosis of cancer may clarify whether a mutual cause exists, and may also guide clinicians about time windows of high risk of cancer occurrence. Methods and Results We conducted a population-based cohort study among 26 222 men and 28 879 women free of AF and cancer at baseline based on the Danish Diet, Cancer and Health study. The participants were followed for the development of AF (the Danish National Patient Registry) and subsequent cancer (the Danish Cancer Registry) until 2013. We used Cox proportional hazard models with new-onset AF as time-dependent exposure. The men (median age 56 years) and women (median age 56 years) were followed for medians of 16.7 and 19.6 years, respectively. AF was associated with higher risks of any type of cancer (men: hazard ratio [ HR ] 1.41, 95% confidence interval [ CI ], 1.26-1.58; women: HR 1.15, 95% CI , 1.02-1.32), and for men only, lung ( HR 1.66, 95% CI , 1.19-2.30), and colorectal cancer ( HR 1.37, 95% CI , 1.02-1.85). Within the initial 90 days following the diagnosis of AF , the risks of any type of cancer (men: HR 2.89, 95% CI , 2.10-3.98; women: HR 3.72, 95% CI , 2.49-5.56), lung (men: HR 7.70, 95% CI , 4.34-13.68; women: HR 7.98, 95% CI , 3.96-16.09), and colorectal cancer (men: HR 3.35, 95% CI , 1.03-10.90; women: HR 5.91, 95% CI , 2.44-14.29) were higher for men and women. Conclusions A diagnosis of AF is associated with a higher incidence rate of cancer among men and women. The cancer incidence rate is particularly elevated within 90 days after the diagnosis of AF .
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; cancer and stroke; epidemiology; men; women.
Figures

References
-
- Schnabel RB, Yin X, Gona P, Larson MG, Beiser AS, McManus DD, Newton‐Cheh C, Lubitz SA, Magnani JW, Ellinor PT, Seshadri S, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. 50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Framingham heart study: a cohort study. Lancet. 2015;386:154–162. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Heeringa J, van der Kuip DA, Hofman A, Kors JA, van Herpen G, Stricker BH, Stijnen T, Lip GY, Witteman JC. Prevalence, incidence and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation: the Rotterdam study. Eur Heart J. 2006;27:949–953. - PubMed
-
- Lloyd‐Jones DM, Wang TJ, Leip EP, Larson MG, Levy D, Vasan RS, D'Agostino RB, Massaro JM, Beiser A, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ. Lifetime risk for development of atrial fibrillation: the Framingham heart study. Circulation. 2004;110:1042–1046. - PubMed
-
- Kirchhof P, Benussi S, Kotecha D, Ahlsson A, Atar D, Casadei B, Castella M, Diener HC, Heidbuchel H, Hendriks J, Hindricks G, Manolis AS, Oldgren J, Popescu BA, Schotten U, Van Putte B, Vardas P, Agewall S, Camm J, Baron Esquivias G, Budts W, Carerj S, Casselman F, Coca A, De Caterina R, Deftereos S, Dobrev D, Ferro JM, Filippatos G, Fitzsimons D, Gorenek B, Guenoun M, Hohnloser SH, Kolh P, Lip GY, Manolis A, McMurray J, Ponikowski P, Rosenhek R, Ruschitzka F, Savelieva I, Sharma S, Suwalski P, Tamargo JL, Taylor CJ, Van Gelder IC, Voors AA, Windecker S, Zamorano JL, Zeppenfeld K. 2016 ESC guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with EACTS. Eur Heart J. 2016;37:2893–2962. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

