Baseline Longitudinal Strain Predicts Recovery of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Hospitalized Patients With Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy
- PMID: 30371257
- PMCID: PMC6474980
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009841
Baseline Longitudinal Strain Predicts Recovery of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction in Hospitalized Patients With Nonischemic Cardiomyopathy
Abstract
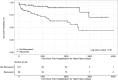
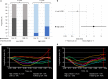
Background Heart failure ( HF ) with "recovered" ejection fraction ( HF rec EF ) is an emerging phenotype, but no tools exist to predict ejection fraction ( EF ) recovery in acute HF . We hypothesized that indices of baseline cardiac structure and function predict HF rec EF in nonischemic cardiomyopathy and reduced EF . Methods and Results We identified a nonischemic cardiomyopathy cohort with EF <40% during the first HF hospitalization (n=166). We performed speckle-tracking echocardiography to measure longitudinal, circumferential, and radial strain, and the average of these measures (myocardial systolic performance). HF rec EF was defined as follow-up EF ≥40% and ≥10% improvement from baseline EF . Fifty-nine patients (36%) achieved HF rec EF (baseline EF 26±7%; follow-up EF 51±7%) within a median of 135 (interquartile range 58-239) days after the first HF hospitalization. Baseline demographics, biomarker profiles, and comorbid conditions (except lower chronic kidney disease in HF rec EF ) were similar between HF rec EF and persistent reduced- EF groups. HF rec EF patients had smaller baseline left ventricular end-systolic dimension (3.6 versus 4.8 cm; P<0.01), higher baseline myocardial systolic performance (9.2% versus 8.1%; P=0.02), and improved survival (adjusted hazard ratio 0.27, 95% confidence interval 0.11, 0.62). We found a significant interaction between baseline left ventricular end-systolic dimension and absolute longitudinal strain. Among patients with left ventricular end-systolic dimension >4.35 cm, higher absolute longitudinal strain (≥8%) was associated with HF rec EF (unadjusted odds ratio=3.9, 95% CI )confidence interval 1.2, 12.8). Incorporation of baseline indices of cardiac mechanics with clinical variables resulted in a predictive model for HF rec EF with c-statistic=0.85. Conclusions Factors associated with achieving HF rec EF were specific to cardiac structure and indices of cardiac mechanics. Higher baseline absolute longitudinal strain is associated with HF rec EF among nonischemic cardiomyopathy patients with reduced EF and larger left ventricular dimensions.
Keywords: echocardiography; heart failure with recovered ejection fraction; longitudinal strain; nonischemic heart failure; recovery.
Figures
References
-
- Wilcox JE, Yancy CW. Heart failure—a new phenotype emerges. JAMA Cardiol. 2016;1:507–509. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL; American College of Cardiology Foundation and American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines . 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62:e147–e239. - PubMed
-
- Yancy CW, Jessup M, Bozkurt B, Butler J, Casey DE Jr, Drazner MH, Fonarow GC, Geraci SA, Horwich T, Januzzi JL, Johnson MR, Kasper EK, Levy WC, Masoudi FA, McBride PE, McMurray JJ, Mitchell JE, Peterson PN, Riegel B, Sam F, Stevenson LW, Tang WH, Tsai EJ, Wilkoff BL. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation. 2013;128:1810–1852. - PubMed
-
- Kalogeropoulos AP, Fonarow GC, Georgiopoulou V, Burkman G, Siwamogsatham S, Patel A, Li S, Papadimitriou L, Butler J. Characteristics and outcomes of adult outpatients with heart failure and improved or recovered ejection fraction. JAMA Cardiol. 2016;1:510–518. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

