Use of Antihypertensive Agents and Association With Risk of Adverse Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
- PMID: 30371331
- PMCID: PMC6404880
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.009992
Use of Antihypertensive Agents and Association With Risk of Adverse Outcomes in Chronic Kidney Disease: Focus on Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
Abstract
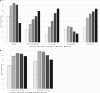
Background Our objective was to determine patterns of antihypertensive agent use by stage of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and to evaluate the association between different classes of antihypertensive agents with nonrenal outcomes, especially in advanced CKD . Methods and Results We studied 3939 participants of the CRIC (Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort) study. Predictors were time-dependent angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker , β-blocker, and calcium channel blocker use (versus nonuse of agents in each class). Outcomes were adjudicated heart failure events or death. Adjusted Cox models were used to determine the association between predictors and outcomes. We also examined whether the associations differed based on the severity of CKD (early [stage 2-3 CKD ] versus advanced disease [stage 4-5 CKD ]). During median follow-up of 7.5 years, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor use plateaued during CKD stage 3 (75%) and declined to 37% by stage 5, while β-blocker, calcium channel blocker, and diuretic use increased steadily with advancing CKD . Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitor use was associated with lower risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.67-0.97) and death (hazard ratio, 0.78; 95% confidence interval, 0.67-0.90), regardless of severity of CKD . Calcium channel blocker use was not associated with risk of heart failure or death, regardless of the severity of CKD . β-Blocker use was associated with higher risk of heart failure (hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% confidence interval, 1.29-2.04) and death (hazard ratio, 1.22; 95% confidence interval, 1.03-1.43), especially during early CKD ( P<0.05 for interaction). Conclusions Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and angiotensin receptor blocker use decreased, while use of other agents increased with advancing CKD . Use of agents besides angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers may be associated with suboptimal outcomes in patients with CKD .
Keywords: heart failure; hypertension; kidney.
Figures
References
-
- Whelton PK, Carey RM, Aronow WS, Casey DE Jr, Collins KJ, Dennison Himmelfarb C, DePalma SM, Gidding S, Jamerson KA, Jones DW, MacLaughlin EJ, Muntner P, Ovbiagele B, Smith SC Jr, Spencer CC, Stafford RS, Taler SJ, Thomas RJ, Williams KA Sr, Williamson JD, Wright JT Jr. 2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APHA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA guideline for the prevention, detection, evaluation, and management of high blood pressure in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Hypertension. 2018;71:e13–e115. - PubMed
-
- Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, Remuzzi G, Snapinn SM, Zhang Z, Shahinfar S. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–869. - PubMed
-
- Lewis EJ, Hunsicker LG, Clarke WR, Berl T, Pohl MA, Lewis JB, Ritz E, Atkins RC, Rohde R, Raz I. Renoprotective effect of the angiotensin‐receptor antagonist irbesartan in patients with nephropathy due to type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:851–860. - PubMed
-
- Remuzzi G, Chiurchiu C, Ruggenenti P. Proteinuria predicting outcome in renal disease: nondiabetic nephropathies (REIN). Kidney Int Suppl. 2004;92:S90–S96. - PubMed
-
- Weir MR, Lakkis JI, Jaar B, Rocco MV, Choi MJ, Mattrix‐Kramer H, Ku E. Use of renin‐angiotensin system blockade in advanced ckd: An NKF‐KDOQI controversies report. Am J Kidney Dis. Available at: https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/american-journal-of-kidney-disease.... Accessed September 20, 2018. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

