Abnormal protein and mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines in the prefrontal cortex of depressed individuals who died by suicide
- PMID: 30371993
- PMCID: PMC6203549
- DOI: 10.1503/jpn.170192
Abnormal protein and mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines in the prefrontal cortex of depressed individuals who died by suicide
Abstract
Background: Depression and stress are major risk factors for suicidal behaviour, and some studies show abnormalities of proinflammatory cytokines in the serum and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of depressed and suicidal patients. However, it is not clear if similar abnormalities of cytokines are present in the brain of suicidal and depressed patients.
Methods: We therefore determined the mRNA (using realtime polymerase chain reaction) and protein (using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and Western Blot) expression levels of interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-α, lymphotoxin A, lymphotoxin B, IL-8, IL-10 and IL-13 in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) obtained from 24 depressed individuals who died by suicide and 24 nonpsychiatric controls.
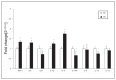
Results: We observed that the mRNA and protein levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and lymphotoxin A were significantly increased, and levels of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10, and of IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1RA) were significantly decreased in the PFC of depressed individuals who died by suicide compared with controls. There were no significant differences in the protein and mRNA levels of IL-8 and IL-13 in the PFC.
Limitations: The main limitation of this study is that some of the suicide group had been taking antidepressant medication at the time of death.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that alterations of cytokines may be associated with the pathophysiology of depressed suicide and there may be an imbalance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in people who die by suicide. The causes of these increases in the brain of people who die by suicide, therefore, need to be investigated further.
© 2018 Joule Inc. or its licensors
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Center for Injury Prevention and Control. Web-based Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System (WISQARS) [accessed 2017 Sept 20]. Available: www.cdc.gov/ncipc/wisqars.
-
- Howren MB, Lamkin DM, Suls J. Associations of depression with C-reactive protein, IL-1, and IL-6: a meta-analysis. Psychosom Med. 2009;71:171–86. - PubMed
-
- Valkanova V, Ebmeier KP, Allan CL. CRP, IL-6 and depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Affect Disord. 2013;150:736–44. - PubMed
-
- Dantzer R. Cytokine-induced sickness behavior: mechanisms and implications. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;933:222–34. - PubMed
-
- Dieperink E, Ho SB, Tetrick L, et al. Suicidal ideation during interferon-alpha2b and ribavirin treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gen Hosp Psychiatry. 2004;26:237–40. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

