The development of two field-ready reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for the rapid detection of Seneca Valley virus 1
- PMID: 30372584
- PMCID: PMC6434928
- DOI: 10.1111/tbed.13051
The development of two field-ready reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification assays for the rapid detection of Seneca Valley virus 1
Abstract
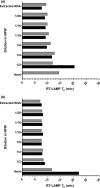
Seneca Valley virus 1 (SVV-1) has been associated with vesicular disease in swine, with clinical signs indistinguishable from those of other notifiable vesicular diseases such as foot-and-mouth disease. Rapid and accurate detection of SVV-1 is central to confirm the disease causing agent, and to initiate the implementation of control processes. The development of rapid, cost-effective diagnostic assays that can be used at the point of sample collection has been identified as a gap in preparedness for the control of SVV-1. This study describes the development and bench validation of two reverse transcription loop-mediated amplification (RT-LAMP) assays targeting the 5'-untranslated region (5'-UTR) and the VP3-1 region for the detection of SVV-1 that may be performed at the point of sample collection. Both assays were able to demonstrate amplification of all neat samples diluted 1/100 in negative pig epithelium tissue suspension within 8 min, when RNA was extracted prior to the RT-LAMP assay, and no amplification was observed for the other viruses tested. Simple sample preparation methods using lyophilized reagents were investigated, to negate the requirement for RNA extraction. Only a small delay in the time to amplification was observed for these lyophilized reagents, with a time from sample receipt to amplification achieved within 12 min. Although diagnostic validation is recommended, these RT-LAMP assays are highly sensitive and specific, with the potential to be a useful tool in the rapid diagnosis of SVV-1 in the field.
Keywords: Seneca Valley virus-1; point-of-care diagnostics; rapid detection; reverse transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification.
© 2018 Blackwell Verlag GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Duncan Clark and Nick Morant have a commercial interest in OptiGene Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Ambagala, A. , Fisher, M. , Goolia, M. , Nfon, C. , Furukawa‐Stoffer, T. , Ortega Polo, R. , & Lung, O. (2016). Field‐Deployable Reverse Transcription‐Insulated Isothermal PCR (RT‐iiPCR) Assay for rapid and sensitive detection of foot‐and‐mouth disease virus. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 64, 1610–1623. 10.1111/tbed.12554 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson, I. (2002). Foot and Mouth Disease 2001: Lessons to be Learned Inquiry Report. London, UK: The Stationery Office, HC 888 Session 2001–2002.
-
- Armson, B. , Fowler, V. L. , Tuppurainen, E. S. M. , Howson, E. L. A. , Madi, M. , Sallu, R. , … King, D. P. (2017). Detection of Capripoxvirus DNA Using a Field‐Ready Nucleic Acid Extraction and Real‐Time PCR Platform. Transboundary and Emerging Diseases, 64(3), 994–997. 10.1111/tbed.12447 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

