Interactive Roles for AMPK and Glycogen from Cellular Energy Sensing to Exercise Metabolism
- PMID: 30373152
- PMCID: PMC6274970
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19113344
Interactive Roles for AMPK and Glycogen from Cellular Energy Sensing to Exercise Metabolism
Abstract
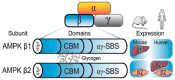
The AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is a heterotrimeric complex with central roles in cellular energy sensing and the regulation of metabolism and exercise adaptations. AMPK regulatory β subunits contain a conserved carbohydrate-binding module (CBM) that binds glycogen, the major tissue storage form of glucose. Research over the past two decades has revealed that the regulation of AMPK is impacted by glycogen availability, and glycogen storage dynamics are concurrently regulated by AMPK activity. This growing body of research has uncovered new evidence of physical and functional interactive roles for AMPK and glycogen ranging from cellular energy sensing to the regulation of whole-body metabolism and exercise-induced adaptations. In this review, we discuss recent advancements in the understanding of molecular, cellular, and physiological processes impacted by AMPK-glycogen interactions. In addition, we appraise how novel research technologies and experimental models will continue to expand the repertoire of biological processes known to be regulated by AMPK and glycogen. These multidisciplinary research advances will aid the discovery of novel pathways and regulatory mechanisms that are central to the AMPK signaling network, beneficial effects of exercise and maintenance of metabolic homeostasis in health and disease.
Keywords: AMP-activated protein kinase; cellular energy sensing; energy utilization; exercise; glycogen; glycogen storage disease; liver; metabolic disease; metabolism; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oakhill J.S., Chen Z.P., Scott J.W., Steel R., Castelli L.A., Ling N., Macaulay S.L., Kemp B.E. β-Subunit myristoylation is the gatekeeper for initiating metabolic stress sensing by AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2010;107:19237–19241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1009705107. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Haro L., Garcia-Gimeno M.A., Neumann D., Beullens M., Bollen M., Sanz P. The PP1-R6 protein phosphatase holoenzyme is involved in the glucose-induced dephosphorylation and inactivation of AMP-activated protein kinase, a key regulator of insulin secretion, in MIN6 β cells. FASEB J. 2010;24:5080–5091. doi: 10.1096/fj.10-166306. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

