Synthesis and Evaluation of Spumigin Analogues Library with Thrombin Inhibitory Activity
- PMID: 30373260
- PMCID: PMC6266488
- DOI: 10.3390/md16110413
Synthesis and Evaluation of Spumigin Analogues Library with Thrombin Inhibitory Activity
Abstract
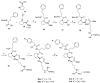
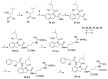
Spumigins are marine natural products derived from cyanobacteria Nodularia spumigena, which mimics the structure of the d-Phe-Pro-Arg sequence and is crucial for binding to the active site of serine proteases thrombin and factor Xa. Biological evaluation of spumigins showed that spumigins with a (2S,4S)-4-methylproline central core represent potential lead compounds for the development of a new structural type of direct thrombin inhibitors. Herein, we represent synthesis and thrombin inhibitory activity of a focused library of spumigins analogues with indoline ring or l-proline as a central core. Novel compounds show additional insight into the structure and biological effects of spumigins. The most active analogue was found to be a derivative containing l-proline central core with low micromolar thrombin inhibitory activity.
Keywords: marine products; natural peptides; peptidomimetics; thrombin inhibition.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synthesis of potential thrombin inhibitors. Incorporation of tartaric acid templates as P2 proline mimetics.Bioorg Med Chem. 2002 May;10(5):1567-80. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00426-6. Bioorg Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 11886818
-
In-depth study of tripeptide-based alpha-ketoheterocycles as inhibitors of thrombin. Effective utilization of the S1' subsite and its implications to structure-based drug design.J Med Chem. 2005 Mar 24;48(6):1984-2008. doi: 10.1021/jm0303857. J Med Chem. 2005. PMID: 15771442
-
Selection of S18326 as a new potent and selective boronic acid direct thrombin inhibitor.Thromb Haemost. 1997 Oct;78(4):1221-7. Thromb Haemost. 1997. PMID: 9364988
-
Chemistry and biology of the peptide anticoagulant D-MePhe-Pro-Arg-H (GYKI-14766).Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;340:91-108. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4899-2418-6_9. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993. PMID: 8154347 Review. No abstract available.
-
Natural Proline-Rich Cyclopolypeptides from Marine Organisms: Chemistry, Synthetic Methodologies and Biological Status.Mar Drugs. 2016 Oct 26;14(11):194. doi: 10.3390/md14110194. Mar Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27792168 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Marine Natural Products and Coronary Artery Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 21;8:739932. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.739932. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34621803 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burja A.M., Banaigs B., Grant Burgess J. Marine cyanobacteria—A prolific source of natural products. Tetrahedron. 2001;57:9347–9377. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4020(01)00931-0. - DOI
-
- Fujii K., Sivonen K., Adachi K., Noguchi K., Sano H., Hirayama K., Suzuki M., Harada K.-I. Comparative study of toxic and non-toxic cyanobacteria products: Novel peptides from toxic Nodularia spumigena AV1. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997;38:5525–5528. doi: 10.1016/S0040-4039(97)01192-1. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

